# 哈希表(散列表)
## 简介
哈希表也叫散列表,是根据关键值key直接进行访问的数据结构。它通过把key映射到表中一个位置来记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
## 哈希冲突解决方法
散列函数对不同的键值key映射可能得到一样的值,这就产生哈希冲突。解决哈希冲突的方法主要有以下两种:
* 开放定址法
线性探测法:当我们往散列表中插入数据时,如果某个数据经过散列函数散列之后,存储位置已经被占用了,我们就从当前位置开始,依次往后查找,看是否有空闲位置,直到找到为止。
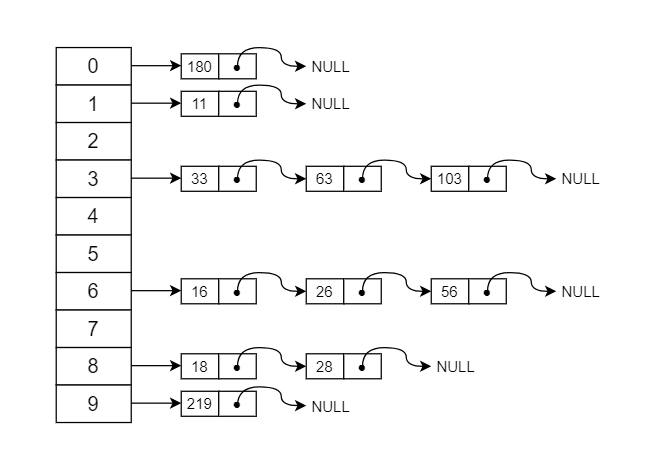
* 链地址法
将哈希冲突的数据用链表保存起来,很多语言和系统采用这种方法解决哈希冲突,原理如下图
## 代码实现
```
#ifndef Hashmap_H
#define Hashmap_H
/*
* @brief 链地址法实现哈希表
* @param Key: 键值
* @param Value: 值
* @param HashFunc: 哈希函数
*/
template <typename Key, typename Value, typename HashFunc>
class Hashmap {
public:
struct Node {
Node(Key key, Value value)
: key(key), value(value), next(nullptr) {}
Key key;
Value value;
Node *next;
};
public:
Hashmap(size_t size) : size(size), hash()
{
table = new Node*[size];
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
table[i] = nullptr;
}
~Hashmap()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
Node* node = table[i];
while (node)
{
Node* delNode = node;
node = node->next;
delete delNode;
}
}
delete[] table;
}
void insert(const Key& key, const Value& value)
{
int index = hash(key) % size;
Node* node = new Node(key, value);
node->next = table[index];
table[index] = node;
}
bool remove(const Key& key)
{
unsigned index = hash(key) % size;
Node* node = table[index];
Node* prev = nullptr;
while (node)
{
if (node->key == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
table[index] = node->next;
else
prev->next = node->next;
delete node;
return true;
}
prev = node;
node = node->next;
}
return false;
}
Value* find(const Key& key)
{
unsigned index = hash(key) % size;
if (table[index] != nullptr)
{
Node* node = table[index];
while (node)
{
if (node->key == key)
return &node->value;
node = node->next;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
Value& operator[](const Key& key)
{
unsigned index = hash(key) % size;
if (table[index] != nullptr)
{
Node* node = table[index];
while (node)
{
if (node->key == key)
return node->value;
node = node->next;
}
}
Node* node = new Node(key, Value());
node->next = table[index];
table[index] = node;
return node->value;
}
private:
HashFunc hash;
Node** table;
size_t size;
};
#endif
```
## 测试验证
```
#include <cassert>
#include <iostream>
#include "hashmap.h"
template <class Key>
struct Hash { };
inline size_t __stl_hash_string(const char* s)
{
unsigned long h = 0;
for ( ; *s; ++s)
h = 5*h + *s;
return size_t(h);
}
// std::string偏特化,简单测试只写std::string的特化版本
template <>
struct Hash<std::string> {
size_t operator()(const std::string& s)
{
return __stl_hash_string(s.c_str());
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Hashmap<std::string, std::string, Hash<std::string> > hashmap(10);
hashmap.insert("even", "1225");
hashmap.insert("leo", "1226");
hashmap.insert("cary", "1227");
hashmap.insert("lory", "1228");
assert(*hashmap.find("leo") == "1226");
assert(hashmap.find("lee") == nullptr);
assert(hashmap["even"] == "1225");
}
```
测试通过!
- 空白目录
- 算法
- 排序
- 冒泡排序
- 选择排序
- 插入排序
- 归并排序
- 快速排序
- 计数排序
- 桶排序
- 基数排序
- 希尔排序
- 堆排序
- 二分查找
- 最小堆
- 最小索引堆
- 平衡二叉树(AVL tree)
- bitmap位图
- 布隆过滤器
- hashmap
- topK
- 跳表
- LRU Cache
- kmp
- 最小堆和堆排序
- 最短路径
- C++
- 运行时类型判断RTTI
- C++反射
- 手动实现智能指针
- 序列化实现
- rpc实现
- std::forward
- 函数指针的妙用
- C/C++
- std::function
- 同步队列
- 线程池实现
- std::promise
- 深入理解虚函数
- extern "C" 关键字讲解
- 大端小端的区别
- 简历
- 简历1
- redis
- 数据结构和对象
- sds
- list
- zskiplist
- 腾讯云redis面试题总结
- redis集群部署
- LeetCode
- 目标
- go基础
- 算法快速入门
- 数据结构篇
- 二叉树
- 链表
- 栈和队列
- 二进制
- 基础算法篇
- 二分搜索
- 排序算法
- 动态规划
- 算法思维
- 递归思维
- 滑动窗口思想
- 二叉搜索树
- 回溯法
- 其他
- 剑指offer
- 笔记
- git代理加速
- Linux
- vim大法
- vscode远程不能跳转
- cmake
- 设计模式
- 单例模式
- 简单工厂模式
- 外观模式
- 适配器模式
- 工厂方法模式
- 抽象工厂模式
- 生成器模式
- 原型模式
- 中介者模式
- 观察者模式
- 访问者模式
- 命令模式
- 网络编程
- epoll reactor模式
- linux timerfd系列函数总结
- IO
- mapreduce
- 反射器
- leo通信库
- Mutex
- Condition
- thread
- raft
- 协程
- hook
- 定时器
- 别人的面试经验
- 面试题
- vector崩溃问题
- JAVA
- Linux java环境配置
- ucore
- lab1
- FreeNOS
- leveldb
- 刷题笔记
- 回文串
- 前缀树
- 字符串查找
- 查找两个字符串a,b中的最长公共子串
- 动态规划
- golang
- 顺序循环打印实现
- 数据结构
- rpc运用
- python
- 单例
- 深拷贝浅拷贝
- 链表
- python基础题
- mysql
- 事务
- Linux
- 共享内存
- 刷题记录
- 贪心算法
- 动态规划
- 面试
- 腾讯C++面试
- 微众面试JD
- 迅雷网络面试
- 学习网址
- rabbitMq
