http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_tutorial_8zh-cn.html
本教程简介文件对象模型(Document Object Model, DOM)API。
如[用法一览](http://rapidjson.org/readme.zh-cn.md#%E7%94%A8%E6%B3%95%E4%B8%80%E8%A7%88)中所示,可以解析一个 JSON 至 DOM,然后就可以轻松查询及修改 DOM,并最终转换回 JSON。
# Value 及 Document
每个 JSON 值都储存为`Value`类,而`Document`类则表示整个 DOM,它存储了一个 DOM 树的根`Value`。RapidJSON 的所有公开类型及函数都在`rapidjson`命名空间中。
# 查询 Value
在本节中,我们会使用到`example/tutorial/tutorial.cpp`中的代码片段。
假设我们用 C 语言的字符串储存一个 JSON(`const char* json`):
{
"hello": "world",
"t": true ,
"f": false,
"n": null,
"i": 123,
"pi": 3.1416,
"a": \[1, 2, 3, 4\]
}
把它解析至一个`Document`:
#include "[rapidjson/document.h](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/document_8h.html)"
using namespace [rapidjson](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html);
// ...
[Document](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/classrapidjson_1_1_generic_document.html) document;
document.[Parse](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/classrapidjson_1_1_generic_document.html#aea842b533a858c9a3861451ad9e8642c)(json);
那么现在该 JSON 就会被解析至`document`中,成为一棵 \*DOM 树 \*:
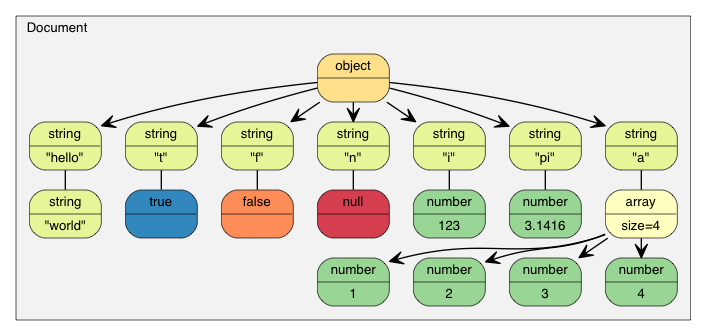
教程中的 DOM
自从 RFC 7159 作出更新,合法 JSON 文件的根可以是任何类型的 JSON 值。而在较早的 RFC 4627 中,根值只允许是 Object 或 Array。而在上述例子中,根是一个 Object。
assert(document.IsObject());
让我们查询一下根 Object 中有没有`"hello"`成员。由于一个`Value`可包含不同类型的值,我们可能需要验证它的类型,并使用合适的 API 去获取其值。在此例中,`"hello"`成员关联到一个 JSON String。
assert(document.[HasMember](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/classrapidjson_1_1_generic_value.html#aa78e2eb30c6b918826eccf03f04f166b)("hello"));
assert(document\["hello"\].IsString());
printf("hello = %s\\n", document\["hello"\].GetString());
world
JSON True/False 值是以`bool`表示的。
assert(document\["t"\].IsBool());
printf("t = %s\\n", document\["t"\].GetBool() ? "true" : "false");
true
JSON Null 值可用`IsNull()`查询。
printf("n = %s\\n", document\["n"\].IsNull() ? "null" : "?");
null
JSON Number 类型表示所有数值。然而,C++ 需要使用更专门的类型。
assert(document\["i"\].IsNumber());
// 在此情况下,IsUint()/IsInt64()/IsUInt64() 也会返回 true
assert(document\["i"\].IsInt());
printf("i = %d\\n", document\["i"\].GetInt());
// 另一种用法: (int)document\["i"\]
assert(document\["pi"\].IsNumber());
assert(document\["pi"\].IsDouble());
printf("pi = %g\\n", document\["pi"\].GetDouble());
i = 123
pi = 3.1416
JSON Array 包含一些元素。
// 使用引用来连续访问,方便之余还更高效。
const [Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505)& a = document\["a"\];
assert(a.IsArray());
for ([SizeType](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#a44eb33eaa523e36d466b1ced64b85c84) i = 0; i < a.Size(); i++) // 使用 SizeType 而不是 size\_t
printf("a\[%d\] = %d\\n", i, a\[i\].GetInt());
a\[0\] = 1
a\[1\] = 2
a\[2\] = 3
a\[3\] = 4
注意,RapidJSON 并不自动转换各种 JSON 类型。例如,对一个 String 的 Value 调用`GetInt()`是非法的。在调试模式下,它会被断言失败。在发布模式下,其行为是未定义的。
以下将会讨论有关查询各类型的细节。
## 查询 Array
缺省情况下,`SizeType`是`unsigned`的 typedef。在多数系统中,Array 最多能存储 2^32-1 个元素。
你可以用整数字面量访问元素,如`a[0]`、`a[1]`、`a[2]`。
Array 与`std::vector`相似,除了使用索引,也可使用迭代器来访问所有元素。
for (Value::ConstValueIterator itr = a.Begin(); itr != a.End(); ++itr)
printf("%d ", itr->GetInt());
还有一些熟悉的查询函数:
* `SizeType Capacity() const`
* `bool Empty() const`
### 范围 for 循环 (v1.1.0 中的新功能)
当使用 C++11 功能时,你可使用范围 for 循环去访问 Array 内的所有元素。
for (auto& v : a.GetArray())
printf("%d ", v.GetInt());
## 查询 Object
和 Array 相似,我们可以用迭代器去访问所有 Object 成员:
static const char\* kTypeNames\[\] =
{ "Null", "False", "True", "Object", "Array", "String", "Number" };
for (Value::ConstMemberIterator itr = document.[MemberBegin](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/classrapidjson_1_1_generic_value.html#ae89a77887aa3eb1f1f913727cbff6786)();
itr != document.[MemberEnd](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/classrapidjson_1_1_generic_value.html#a34ee3d75a7aa308043fb34b0743bfe7c)(); ++itr)
{
printf("Type of member %s is %s\\n",
itr->name.GetString(), kTypeNames\[itr->value.GetType()\]);
}
Type of member hello is String
Type of member t is True
Type of member f is False
Type of member n is Null
Type of member i is Number
Type of member pi is Number
Type of member a is Array
注意,当`operator[](const char*)`找不到成员,它会断言失败。
若我们不确定一个成员是否存在,便需要在调用`operator[](const char*)`前先调用`HasMember()`。然而,这会导致两次查找。更好的做法是调用`FindMember()`,它能同时检查成员是否存在并返回它的 Value:
Value::ConstMemberIterator itr = document.[FindMember](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/classrapidjson_1_1_generic_value.html#ad22fdeac87ec6c370dd43075d3586811)("hello");
if (itr != document.[MemberEnd](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/classrapidjson_1_1_generic_value.html#a34ee3d75a7aa308043fb34b0743bfe7c)())
printf("%s\\n", itr->value.GetString());
### 范围 for 循环 (v1.1.0 中的新功能)
当使用 C++11 功能时,你可使用范围 for 循环去访问 Object 内的所有成员。
for (auto& m : document.GetObject())
printf("Type of member %s is %s\\n",
m.name.GetString(), kTypeNames\[m.value.GetType()\]);
## 查询 Number
JSON 只提供一种数值类型──Number。数字可以是整数或实数。RFC 4627 规定数字的范围由解析器指定。
由于 C++ 提供多种整数及浮点数类型,DOM 尝试尽量提供最广的范围及良好性能。
当解析一个 Number 时, 它会被存储在 DOM 之中,成为下列其中一个类型:
| 类型 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| `unsigned` | 32 位无号整数 |
| `int` | 32 位有号整数 |
| `uint64_t` | 64 位无号整数 |
| `int64_t` | 64 位有号整数 |
| `double` | 64 位双精度浮点数 |
当查询一个 Number 时, 你可以检查该数字是否能以目标类型来提取:
| 查检 | 提取 |
| --- | --- |
| `bool IsNumber()` | 不适用 |
| `bool IsUint()` | `unsigned GetUint()` |
| `bool IsInt()` | `int GetInt()` |
| `bool IsUint64()` | `uint64_t GetUint64()` |
| `bool IsInt64()` | `int64_t GetInt64()` |
| `bool IsDouble()` | `double GetDouble()` |
注意,一个整数可能用几种类型来提取,而无需转换。例如,一个名为`x`的 Value 包含 123,那么`x.IsInt() == x.IsUint() == x.IsInt64() == x.IsUint64() == true`。但如果一个名为`y`的 Value 包含 -3000000000,那么仅会令`x.IsInt64() == true`。
当要提取 Number 类型,`GetDouble()`是会把内部整数的表示转换成`double`。注意`int`和`unsigned`可以安全地转换至`double`,但`int64_t`及`uint64_t`可能会丧失精度(因为`double`的尾数只有 52 位)。
## 查询 String
除了`GetString()`,`Value`类也有一个`GetStringLength()`。这里会解释个中原因。
根据 RFC 4627,JSON String 可包含 Unicode 字符`U+0000`,在 JSON 中会表示为`"\u0000"`。问题是,C/C++ 通常使用空字符结尾字符串(null-terminated string),这种字符串把 ``\0'`作为结束符号。
为了符合 RFC 4627,RapidJSON 支持包含`U+0000`的 String。若你需要处理这些 String,便可使用`GetStringLength()`去获得正确的字符串长度。
例如,当解析以下的 JSON 至`Document d`之后:
{ "s" : "a\\u0000b" }
`"a\u0000b"`值的正确长度应该是 3。但`strlen()`会返回 1。
`GetStringLength()`也可以提高性能,因为用户可能需要调用`strlen()`去分配缓冲。
此外,`std::string`也支持这个构造函数:
string(const char\* s, size\_t count);
此构造函数接受字符串长度作为参数。它支持在字符串中存储空字符,也应该会有更好的性能。
## 比较两个 Value
你可使用`==`及`!=`去比较两个 Value。当且仅当两个 Value 的类型及内容相同,它们才当作相等。你也可以比较 Value 和它的原生类型值。以下是一个例子。
if (document\["hello"\] == document\["n"\]) /\*...\*/; // 比较两个值
if (document\["hello"\] == "world") /\*...\*/; // 与字符串家面量作比较
if (document\["i"\] != 123) /\*...\*/; // 与整数作比较
if (document\["pi"\] != 3.14) /\*...\*/; // 与 double 作比较
Array/Object 顺序以它们的元素/成员作比较。当且仅当它们的整个子树相等,它们才当作相等。
注意,现时若一个 Object 含有重复命名的成员,它与任何 Object 作比较都总会返回`false`。
# 创建/修改值
有多种方法去创建值。 当一个 DOM 树被创建或修改后,可使用`Writer`再次存储为 JSON。
## 改变 Value 类型
当使用默认构造函数创建一个 Value 或 Document,它的类型便会是 Null。要改变其类型,需调用`SetXXX()`或赋值操作,例如:
[Document](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ace11b5b575baf1cccd5ba5f8586dcdc8) d; // Null
d.SetObject();
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) v; // Null
v.SetInt(10);
v = 10; // 简写,和上面的相同
### 构造函数的各个重载
几个类型也有重载构造函数:
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) b(true); // 调用 Value(bool)
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) i(-123); // 调用 Value(int)
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) u(123u); // 调用 Value(unsigned)
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) d(1.5); // 调用 Value(double)
要重建空 Object 或 Array,可在默认构造函数后使用`SetObject()`/`SetArray()`,或一次性使用`Value(Type)`:
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) o([kObjectType](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ae79a4751c1c460ff0de5ecc07874f3e4acf030b422a32c3647c7c5973bd4dd0a9));
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) a([kArrayType](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ae79a4751c1c460ff0de5ecc07874f3e4a058c622e1e7d59419ae58b895cbce468));
## 转移语义(Move Semantics)
在设计 RapidJSON 时有一个非常特别的决定,就是 Value 赋值并不是把来源 Value 复制至目的 Value,而是把来源 Value 转移(move)至目的 Value。例如:
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) a(123);
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) b(456);
b = a; // a 变成 Null,b 变成数字 123。
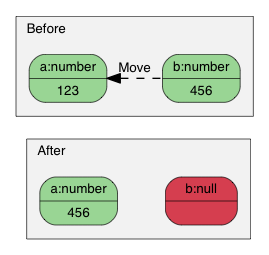
使用移动语义赋值。
为什么?此语义有何优点?
最简单的答案就是性能。对于固定大小的 JSON 类型(Number、True、False、Null),复制它们是简单快捷。然而,对于可变大小的 JSON 类型(String、Array、Object),复制它们会产生大量开销,而且这些开销常常不被察觉。尤其是当我们需要创建临时 Object,把它复制至另一变量,然后再析构它。
例如,若使用正常 \* 复制 \* 语义:
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) o([kObjectType](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ae79a4751c1c460ff0de5ecc07874f3e4acf030b422a32c3647c7c5973bd4dd0a9));
{
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) contacts([kArrayType](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ae79a4751c1c460ff0de5ecc07874f3e4a058c622e1e7d59419ae58b895cbce468));
// 把元素加进 contacts 数组。
// ...
o.AddMember("contacts", contacts, d.GetAllocator()); // 深度复制 contacts (可能有大量内存分配)
// 析构 contacts。
}
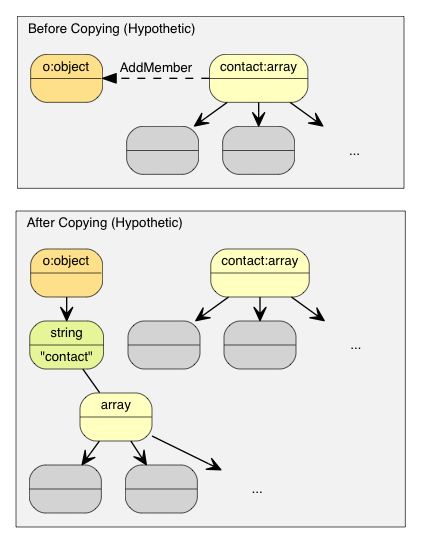
复制语义产生大量的复制操作。
那个`o`Object 需要分配一个和 contacts 相同大小的缓冲区,对 conacts 做深度复制,并最终要析构 contacts。这样会产生大量无必要的内存分配/释放,以及内存复制。
有一些方案可避免实质地复制这些数据,例如引用计数(reference counting)、垃圾回收(garbage collection, GC)。
为了使 RapidJSON 简单及快速,我们选择了对赋值采用 \* 转移 \* 语义。这方法与`std::auto_ptr`相似,都是在赋值时转移拥有权。转移快得多简单得多,只需要析构原来的 Value,把来源`memcpy()`至目标,最后把来源设置为 Null 类型。
因此,使用转移语义后,上面的例子变成:
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) o([kObjectType](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ae79a4751c1c460ff0de5ecc07874f3e4acf030b422a32c3647c7c5973bd4dd0a9));
{
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) contacts([kArrayType](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ae79a4751c1c460ff0de5ecc07874f3e4a058c622e1e7d59419ae58b895cbce468));
// adding elements to contacts array.
o.AddMember("contacts", contacts, d.GetAllocator()); // 只需 memcpy() contacts 本身至新成员的 Value(16 字节)
// contacts 在这里变成 Null。它的析构是平凡的。
}
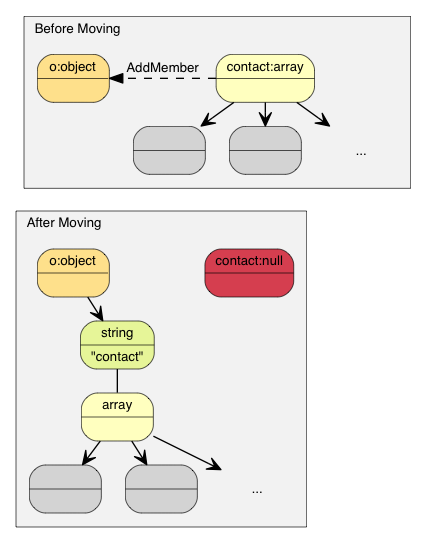
转移语义不需复制。
在 C++11 中这称为转移赋值操作(move assignment operator)。由于 RapidJSON 支持 C++03,它在赋值操作采用转移语义,其它修改型函数如`AddMember()`,`PushBack()`也采用转移语义。
### 转移语义及临时值
有时候,我们想直接构造一个 Value 并传递给一个“转移”函数(如`PushBack()`、`AddMember()`)。由于临时对象是不能转换为正常的 Value 引用,我们加入了一个方便的`Move()`函数:
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) a([kArrayType](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ae79a4751c1c460ff0de5ecc07874f3e4a058c622e1e7d59419ae58b895cbce468));
Document::AllocatorType& allocator = document.[GetAllocator](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/classrapidjson_1_1_generic_document.html#ad92c6cd025d411258d1f2ad890e2ee3f)();
// a.PushBack(Value(42), allocator); // 不能通过编译
a.PushBack([Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505)().SetInt(42), allocator); // fluent API
a.PushBack([Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505)(42).Move(), allocator); // 和上一行相同
## 创建 String
RapidJSON 提供两个 String 的存储策略。
1. copy-string: 分配缓冲区,然后把来源数据复制至它。
2. const-string: 简单地储存字符串的指针。
Copy-string 总是安全的,因为它拥有数据的克隆。Const-string 可用于存储字符串字面量,以及用于在 DOM 一节中将会提到的 in-situ 解析中。
为了让用户自定义内存分配方式,当一个操作可能需要内存分配时,RapidJSON 要求用户传递一个 allocator 实例作为 API 参数。此设计避免了在每个 Value 存储 allocator(或 document)的指针。
因此,当我们把一个 copy-string 赋值时, 调用含有 allocator 的`SetString()`重载函数:
[Document](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ace11b5b575baf1cccd5ba5f8586dcdc8) document;
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) author;
char buffer\[10\];
int len = sprintf(buffer, "%s %s", "Milo", "Yip"); // 动态创建的字符串。
author.SetString(buffer, len, document.GetAllocator());
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
// 清空 buffer 后 author.GetString() 仍然包含 "Milo Yip"
在此例子中,我们使用`Document`实例的 allocator。这是使用 RapidJSON 时常用的惯用法。但你也可以用其他 allocator 实例。
另外,上面的`SetString()`需要长度参数。这个 API 能处理含有空字符的字符串。另一个`SetString()`重载函数没有长度参数,它假设输入是空字符结尾的,并会调用类似`strlen()`的函数去获取长度。
最后,对于字符串字面量或有安全生命周期的字符串,可以使用 const-string 版本的`SetString()`,它没有 allocator 参数。对于字符串字面量(或字符数组常量),只需简单地传递字面量,又安全又高效:
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) s;
s.SetString("rapidjson"); // 可包含空字符,长度在编译萁推导
s = "rapidjson"; // 上行的缩写
对于字符指针,RapidJSON 需要作一个标记,代表它不复制也是安全的。可以使用`StringRef`函数:
const char \* cstr = getenv("USER");
size\_t cstr\_len = ...; // 如果有长度
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) s;
// s.SetString(cstr); // 这不能通过编译
s.SetString([StringRef](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/structrapidjson_1_1_generic_string_ref.html#aa6b9fd9f6aa49405a574c362ba9af6b5)(cstr)); // 可以,假设它的生命周期安全,并且是以空字符结尾的
s = [StringRef](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/structrapidjson_1_1_generic_string_ref.html#aa6b9fd9f6aa49405a574c362ba9af6b5)(cstr); // 上行的缩写
s.SetString([StringRef](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/structrapidjson_1_1_generic_string_ref.html#aa6b9fd9f6aa49405a574c362ba9af6b5)(cstr, cstr\_len));// 更快,可处理空字符
s = [StringRef](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/structrapidjson_1_1_generic_string_ref.html#aa6b9fd9f6aa49405a574c362ba9af6b5)(cstr, cstr\_len); // 上行的缩写
## 修改 Array
Array 类型的 Value 提供与`std::vector`相似的 API。
* `Clear()`
* `Reserve(SizeType, Allocator&)`
* `Value& PushBack(Value&, Allocator&)`
* `template <typename T> GenericValue& PushBack(T, Allocator&)`
* `Value& PopBack()`
* `ValueIterator Erase(ConstValueIterator pos)`
* `ValueIterator Erase(ConstValueIterator first, ConstValueIterator last)`
注意,`Reserve(...)`及`PushBack(...)`可能会为数组元素分配内存,所以需要一个 allocator。
以下是`PushBack()`的例子:
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) a([kArrayType](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ae79a4751c1c460ff0de5ecc07874f3e4a058c622e1e7d59419ae58b895cbce468));
Document::AllocatorType& allocator = document.GetAllocator();
for (int i = 5; i <= 10; i++)
a.PushBack(i, allocator); // 可能需要调用 realloc() 所以需要 allocator
// 流畅接口(Fluent interface)
a.PushBack("Lua", allocator).PushBack("Mio", allocator);
与 STL 不一样的是,`PushBack()`/`PopBack()`返回 Array 本身的引用。这称为流畅接口(\_fluent interface\_)。
如果你想在 Array 中加入一个非常量字符串,或是一个没有足够生命周期的字符串(见[Create String](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_tutorial_8zh-cn.html#CreateString)),你需要使用 copy-string API 去创建一个 String。为了避免加入中间变量,可以就地使用一个[临时值](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_tutorial_8zh-cn.html#TemporaryValues):
// 就地 Value 参数
contact.PushBack([Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505)("copy", document.GetAllocator()).Move(), // copy string
document.GetAllocator());
// 显式 Value 参数
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) val("key", document.GetAllocator()); // copy string
contact.PushBack(val, document.GetAllocator());
## 修改 Object
Object 是键值对的集合。每个键必须为 String。要修改 Object,方法是增加或移除成员。以下的 API 用来增加城员:
* `Value& AddMember(Value&, Value&, Allocator& allocator)`
* `Value& AddMember(StringRefType, Value&, Allocator&)`
* `template <typename T> Value& AddMember(StringRefType, T value, Allocator&)`
以下是一个例子。
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) contact(kObject);
contact.AddMember("name", "Milo", document.GetAllocator());
contact.AddMember("married", true, document.GetAllocator());
使用`StringRefType`作为 name 参数的重载版本与字符串的`SetString`的接口相似。 这些重载是为了避免复制`name`字符串,因为 JSON object 中经常会使用常数键名。
如果你需要从非常数字符串或生命周期不足的字符串创建键名(见[创建 String](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_tutorial_8zh-cn.html#CreateString)),你需要使用 copy-string API。为了避免中间变量,可以就地使用[临时值](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_tutorial_8zh-cn.html#TemporaryValues):
// 就地 Value 参数
contact.AddMember([Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505)("copy", document.GetAllocator()).Move(), // copy string
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505)().Move(), // null value
document.GetAllocator());
// 显式参数
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) key("key", document.GetAllocator()); // copy string name
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) val(42); // 某 Value
contact.AddMember(key, val, document.GetAllocator());
移除成员有几个选择:
* `bool RemoveMember(const Ch* name)`:使用键名来移除成员(线性时间复杂度)。
* `bool RemoveMember(const Value& name)`:除了`name`是一个 Value,和上一行相同。
* `MemberIterator RemoveMember(MemberIterator)`:使用迭代器移除成员(\_ 常数 \_ 时间复杂度)。
* `MemberIterator EraseMember(MemberIterator)`:和上行相似但维持成员次序(线性时间复杂度)。
* `MemberIterator EraseMember(MemberIterator first, MemberIterator last)`:移除一个范围内的成员,维持次序(线性时间复杂度)。
`MemberIterator RemoveMember(MemberIterator)`使用了“转移最后”手法来达成常数时间复杂度。基本上就是析构迭代器位置的成员,然后把最后的成员转移至迭代器位置。因此,成员的次序会被改变。
## 深复制 Value
若我们真的要复制一个 DOM 树,我们可使用两个 APIs 作深复制:含 allocator 的构造函数及`CopyFrom()`。
[Document](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#ace11b5b575baf1cccd5ba5f8586dcdc8) d;
Document::AllocatorType& a = d.GetAllocator();
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) v1("foo");
// Value v2(v1); // 不容许
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) v2(v1, a); // 制造一个克隆
assert(v1.IsString()); // v1 不变
d.SetArray().PushBack(v1, a).PushBack(v2, a);
assert(v1.IsNull() && v2.IsNull()); // 两个都转移动 d
v2.CopyFrom(d, a); // 把整个 document 复制至 v2
assert(d.IsArray() && d.Size() == 2); // d 不变
v1.SetObject().AddMember("array", v2, a);
d.PushBack(v1, a);
## 交换 Value
RapidJSON 也提供`Swap()`。
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) a(123);
[Value](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/namespacerapidjson.html#aa65fc9fb381b2cbc54f98673eadd6505) b("Hello");
a.Swap(b);
assert(a.IsString());
assert(b.IsInt());
无论两棵 DOM 树有多复杂,交换是很快的(常数时间)。
# 下一部分
本教程展示了如何询查及修改 DOM 树。RapidJSON 还有一个重要概念:
1. [流](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_stream_8zh-cn.html)是读写 JSON 的通道。流可以是内存字符串、文件流等。用户也可以自定义流。
2. [编码](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_encoding_8zh-cn.html)定义在流或内存中使用的字符编码。RapidJSON 也在内部提供 Unicode 转换及校验功能。
3. [DOM](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_dom_8zh-cn.html)的基本功能已在本教程里介绍。还有更高级的功能,如原位(\*in situ\*)解析、其他解析选项及高级用法。
4. [SAX](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_sax_8zh-cn.html)是 RapidJSON 解析/生成功能的基础。学习使用`Reader`/`Writer`去实现更高性能的应用程序。也可以使用`PrettyWriter`去格式化 JSON。
5. [性能](http://rapidjson.org/zh-cn/md_doc_performance_8zh-cn.html)展示一些我们做的及第三方的性能测试。
6. 技术内幕 讲述一些 RapidJSON 内部的设计及技术。
- 程序优化
- vtune
- linux性能监控软件Perf
- 系统级性能分析工具perf的介绍与使用
- perf的二级命令
- 全局性概况
- 全局细节
- 最常用功能perf record
- 可视化工具perf timechart
- perf引入的overhead
- perf stat
- gprof
- 三种Linux性能分析工具的比较
- perf+gprof+gprof2dot+graphviz进行性能分析热点
- 英特尔多核平台编程优化大赛报告
- 内存操作
- mmap
- mmap的分类
- 深入理解内存映射mmap
- 计算机底层知识拾遗(九)深入理解内存映射mmap
- 内核驱动mmap Handler利用技术(一)
- Windows内存管理机制及C++内存分配实例
- Linux内存管理初探
- Windows CPU信息查看
- Linux CPU信息查看
- 预留大内存
- Linux下试验大页面映射
- /dev/mem
- Linux中通过/dev/mem操控物理地址
- /dev/mem分析
- 用法举例
- Linux下直接读写物理地址内存
- 查看内存信息
- Cache Memory
- 页面缓存
- 查看各级cache信息的方法
- dmidecode命令查看cache size
- CPU Cache 机制以及 Cache miss
- ARM体系关闭mmu和cache
- CR0-4寄存器介绍
- 查看CR0,CR2,CR3的值
- Linux 下如何禁用CPU cache
- 7个示例科普CPU Cache
- 第一个例子的C代码
- 其中之一
- Linux 从虚拟地址到物理地址
- 内存测试例子
- 每个程序员都应该了解的内存
- Part 1
- 程序员能够做什么
- 3 CPU caches
- 6 What Programmers Can Do
- VirtualAlloc
- Large-Page Support
- Some remarks on VirtualAlloc and MEM_LARGE_PAGES
- DMA
- MOV和MOVS的效率问题?如何高效的拷贝内存 中的数据
- how to use movntdqa to avoid cache pollution
- 计算机底层知识拾遗(一)理解虚拟内存机制
- How to access the control registers cr0,cr2,cr3 from a program
- 细说Cache-L1/L2/L3/TLB
- what-is-the-meaning-of-non-temporal-memory-accesses-in-x86
- How can the L1, L2, L3 CPU caches be turned off on modern x86/amd64 chips?
- UA list
- GDB
- 程序运行参数
- Linux下GDB的多线程调试
- CMake
- CMake快速入门教程:实战
- cmake打印变量值
- function
- source_group
- cmake_parse_arguments
- 编译.S文件
- add_definitions
- CMake添加-g编译选项
- Debug模式下启动
- Mysql
- Mysql联合查询union和union all的使用介绍
- MySQL数据库导入错误:ERROR 1064 (42000) 和 ERROR at line xx: Unknown command '\Z'.
- 解决MYSQL数据库 Table ‘xxx’ is marked as crashed and should be repaired 145错误
- C/C++
- c语言中static的作用
- strlen和sizeof有什么区别?
- printf
- Libuv中文文档之线程
- RapidJSON
- gcc/g++ 实战之编译的四个过程
- __thread
- TARGET_LINK_LIBRARIES
- MAP_HUGETLB
- 使用Intel格式的汇编
- __m128i
- emmintrin.h
- _mm_stream_si128
- _mm_stream_load_si128
- _mm_load_si128
- _mm_xor_si128
- _mm_store_si128
- _mm_cvtsi128_si64
- Intel SSE指令集
- _mm_set_epi64x
- _mm_aesenc_si128
- _umul128
- _mm_malloc
- reinterpret_cast
- strlen
- 读取UTF-8的txt文件发现开头的多三个字节的问题
- PHP
- php计算函数执行时间的方法
- 框架
- Json Rpc远程调用框架
- PHP多进程
- PHP CLI模式下的多进程应用
- php多进程总结
- 优化
- PHP7 优化
- 让你的PHP7更快(GCC PGO)
- PHP的性能演进(从PHP5.0到PHP7.1的性能全评测)
- PHP字符串全排列算法
- 获取服务器基本信息
- cookie
- phpstudy2018 安装xdebug扩展
- 软件下载
- PHP mysqli_error() 函数
- PHP Session 变量
- curl
- curl_getinfo
- 获取请求头
- PHP使用CURL获取302跳转后的地址实例
- PHP基于cURL实现自动模拟登录
- PHP获取远程图片大小(CURL实现)
- CURL模拟登录
- curl模拟登录提交(从目录中获取文件)
- CURL HTTPS
- curl帮v
- rename
- copy
- JSON
- json_encode
- json_decode
- json_last_error_msg
- json_last_error
- PHP json_encode中文乱码解决方法
- var_dump
- PHPStorm与Xdebug设置
- Xdebug原理以notepad为例
- str_pad
- pack
- PHP二进制与字符串之间的相互转换
- PHP执行系统命令(简介及方法)
- 函数
- 十进制转二进制
- 字符串到ASSCI
- 字符串转二进制
- 合并两个表
- 图像识别
- Tesseract
- 虚拟机
- vmware下Kali 2.0安装VMware Tools
- 安装 VMware tools出现“正在进行简易安装时,无法手动启动VMware tools安装”
- 爬虫
- 有哪些好的数据来源或者大数据平台?
- Cygwin
- Git 常用命令
- 排列组合
- 含重复元素序列的全排列
- 全排列的非递归和递归实现(含重复元素)
- GitBook
- 编辑环境
- visual studio code
- 2名数学家或发现史上最快超大乘法运算法,欲破解困扰人类近半个世纪的问题
- 系统预定义常量
- 指令集
- SSE
- _MSC_VER
- msys2
- 安装cmake
- MSYS2 更新源
- 讲Cmake msys32使用问题解答 CXX CMAKE_C_COMPILER配置详解
- VirtualBox
- 解决virtualbox只能安装32位系统的问题
- Ubuntu
- 使用AES-NI的编译参数
- debian下安装内核源码的方法
- tar.xz结尾的文件的解压方法
- Linux命令
- insmod
- fatal error: openssl/bio.h
- 准备module的编译环境(kali)
- Ubuntu/Debian 之内核模块开发准备
- dmesg的详细用法
- Linux系统开机自动加载驱动module
- linux /Module 浅析(转载)
- Kali
- 找回gpedit
- Enable the Lock Pages in Memory Option (Windows)
- TLA
- 双系统
- 显卡
- 显示no CUDA的解决过程
