# Spring4 + Struts2 + Hibernate 集成教程
> 原文: [https://howtodoinjava.com/struts2/spring-4-struts-2-hibernate-integration-tutorial/](https://howtodoinjava.com/struts2/spring-4-struts-2-hibernate-integration-tutorial/)
以前,我已经介绍了 [**Spring3 + Hibernate 集成**](//howtodoinjava.com/spring/spring-orm/spring-3-and-hibernate-integration-tutorial-with-example/ "Spring3 and hibernate integration tutorial with example")示例和 [**Struts2 helloworld**](//howtodoinjava.com/struts-2/struts-2-hello-world-example-application/ "Struts2 hello world example application") 示例。 在本教程中,我将讨论将 spring 框架与 Struts 和 Hibernate 结合使用时要记住的所有重要点。 另外,请注意,本教程使用了其他次要但很重要的概念,例如日志记录,TLD 的使用和事务以及已集成到本教程中。 因此,请记住还要检查其详细信息。
在本教程中,我将使用简单的功能(例如全部获取,添加和删除)来构建员工管理屏幕。 它看起来像这样:
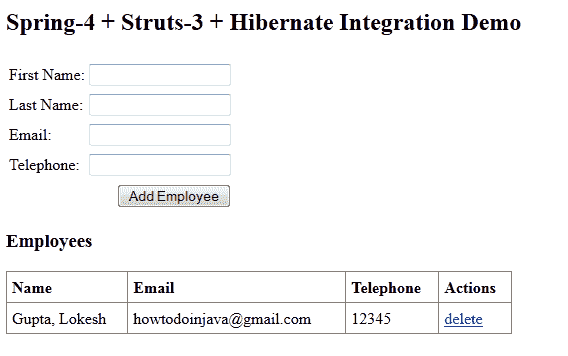
我将按照以下步骤讨论集成过程:
```java
1) Integration Overview
2) Spring + Struts Integration
3) Spring + Hibernate Integration
4) Other Integrated Functionalities
a) Log4j
b) TLDs
c) Transactions
5) Important Points to Keep Remember
6) Database Schema Used in Tutorial
7) 下载源码
```
## 1)概述
在进入集成细节之前,让我们先确定一下***为什么我们需要此集成***本身。 像 Struts 一样,Spring 也可以充当 MVC 实现。 两种框架都有其优缺点,仍然有很多人会同意 **Spring 更好**,并且提供了更广泛的功能。 对我来说,只有两种情况,您需要本教程中提供的信息:
i)您有一个用 Struts 编写的旧应用,并且想要使用 spring 来提高应用的功能很多倍。
ii)您确实想根据自己的原因来学习它。
否则,我不知道为什么有人会在 Spring 选择支柱。 如果您知道其他一些好的理由,请与我们所有人分享。 那挺棒的。
继续,在本教程中,我将**委托从 Struts 到 Spring** 进行动作管理。 进行委派的原因是,通过 Spring 上下文实例化`Action`类时,它可以使用 spring 在其自己的 MVC 实现中为其提供的`Controller`类的所有其他功能。 因此,您将获得所有 spring 功能以及 struts `Action`类,以具有包括`ActionForm`概念在内的控制器逻辑。
## 2)Spring + Struts 集成
这是核心逻辑,从在`web.xml`中注册`ContextLoaderListener`和`StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter`开始。 `ContextLoaderListener`带有初始化参数`contextConfigLocation`,并负责设置和启动 Spring `WebApplicationContext`。 现在,struts 将在与 Spring 相关的服务中特别是在[依赖项注入](//howtodoinjava.com/spring/spring-core/inversion-of-control-ioc-and-dependency-injection-di-patterns-in-spring-framework-and-related-interview-questions/ "Inversion of control (IoC) and dependency injection (DI) patterns in spring framework and related interview questions")中利用此上下文。
`StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter`在类路径中查找`struts.xml`文件,并配置 strut 的特定内容,例如动作映射,全局转发和其他在`struts.xml`文件中定义的内容。
**`web.xml`**
```java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/index.html; id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<display-name>Spring+Struts+Hibernate Integration Example</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>/WEB-INF/index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<!-- Specify the spring context information location;
Default location is applicationContext.xml file in classpath
-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:beans.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- Bootstrap listener to start up and shut down Spring's root WebApplicationContext. -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- Handles both the preparation and execution phases of the Struts dispatching process. -->
<filter>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>debug</param-name>
<param-value>0</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>detail</param-name>
<param-value>0</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!-- Struts Tag Library Descriptors -->
<jsp-config>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/tags/struts-bean</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-bean.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/tags/struts-html</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-html.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/tags/struts-logic</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-logic.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/tags/struts-nested</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-nested.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
</jsp-config>
</web-app>
```
第二步,将在`struts.xml`文件中创建操作映射,如下所示:
**`struts.xml`**
```java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<!-- devMode is helpful when you want some extra logs for debugging -->
<constant name="struts.devMode" value="false" />
<!-- Global message resource;
Otherwise you will have seperate message resource for each Action
-->
<constant name="struts.custom.i18n.resources" value="messages" />
<!--
This is important if you are planning to have slashes in Action URLs
e.g. In this demo, employee is deleted using URL /delete/10
This this is set to false; then struts will try to find mapping for
URL "/10" instaed of "/delete/10"
-->
<constant name="struts.enable.SlashesInActionNames" value="true"/>
<!-- Normal Action mappings are defined here -->
<package name="default" namespace="" extends="struts-default">
<!-- Two things to Notice:
1) class is set to 'editEmployeeAction' which is bean defined by Spring context
2) We have given the method to be called here as well;
-->
<action name="list" class="editEmployeeAction" method="listEmployees">
<result>/view/editEmployeeList.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="add" class="editEmployeeAction" method="addEmployee">
<result type="redirect">/list</result>
</action>
<action name="delete/*" class="editEmployeeAction" method="deleteEmployee">
<param name="employee.id">{1}</param>
<result type="redirect">/list</result>
</action>
<action name="*" class="editEmployeeAction" method="listEmployees">
<result>/view/editEmployeeList.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
```
在单独的 strut 应用程序中,我们将在“`class`”属性中具有完整的`Action`类及其包装信息。 在这里,我们将类名命名为`editEmployeeAction`。 它在哪里定义? 我们将要求 Spring 为我们查找。
Spring 上下文文件`beans.xml`是典型的 Spring 单独上下文文件,具有 Web 应用运行所需的所有内容,其中包括 struts 正在寻找的 bean 定义`editEmployeeAction`。
**`beans.xml`**
```java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:lang="http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/spring-lang.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<!-- This bean has been referred fron struts.xml file; So type it correctly; -->
<!-- Make scope prototype; This is really important. -->
<bean name="editEmployeeAction" class="com.howtodoinjava.controller.EditEmployeeAction" scope="prototype">
<property name="employeeManager">
<ref bean="employeeManager"/>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- These beans are injected automatically by spring context -->
<bean id="employeeDAO" class="com.howtodoinjava.dao.EmployeeDaoImpl">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<bean id="employeeManager" class="com.howtodoinjava.service.EmployeeManagerImpl">
<property name="employeeDAO" ref="employeeDAO"/>
</bean>
<!-- Configure jdbc.properties -->
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"
p:location="/WEB-INF/jdbc.properties" />
<!-- Data Source configuration -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"
p:driverClassName="${jdbc.driverClassName}"
p:url="${jdbc.databaseurl}" p:username="${jdbc.username}"
p:password="${jdbc.password}" />
<!-- Configure hibernate session factory -->
<bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="configLocation">
<value>classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml</value>
</property>
<property name="configurationClass">
<value>org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration</value>
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">${jdbc.dialect}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- Run SQL queries in transactions -->
<tx:annotation-driven />
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
</beans>
```
这是我们要做的**将 Struts 与 spring** 框架集成在一起的所有步骤。 现在,您的动作类如下所示:
**`EditEmployeeAction.java`**
```java
package com.howtodoinjava.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import com.howtodoinjava.entity.EmployeeEntity;
import com.howtodoinjava.service.EmployeeManager;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.Preparable;
public class EditEmployeeAction extends ActionSupport implements Preparable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//Logger configured using log4j
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(EditEmployeeAction.class);
//List of employees; Setter and Getter are below
private List<EmployeeEntity> employees;
//Employee object to be added; Setter and Getter are below
private EmployeeEntity employee;
//Employee manager injected by spring context; This is cool !!
private EmployeeManager employeeManager;
//This method return list of employees in database
public String listEmployees() {
logger.info("listEmployees method called");
employees = employeeManager.getAllEmployees();
return SUCCESS;
}
//This method will be called when a employee object is added
public String addEmployee() {
logger.info("addEmployee method called");
employeeManager.addEmployee(employee);
return SUCCESS;
}
//Deletes a employee by it's id passed in path parameter
public String deleteEmployee() {
logger.info("deleteEmployee method called");
employeeManager.deleteEmployee(employee.getId());
return SUCCESS;
}
//This method will be called before any of Action method is invoked;
//So some pre-processing if required.
@Override
public void prepare() throws Exception {
employee = null;
}
//Getters and Setters hidden
}
```
Spring 还将 DAO 引用注入到`Manager`类。
**`EmployeeManagerImpl.java`**
```java
package com.howtodoinjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.howtodoinjava.dao.EmployeeDAO;
import com.howtodoinjava.entity.EmployeeEntity;
public class EmployeeManagerImpl implements EmployeeManager
{
//Employee dao injected by Spring context
private EmployeeDAO employeeDAO;
//This method will be called when a employee object is added
@Override
@Transactional
public void addEmployee(EmployeeEntity employee) {
employeeDAO.addEmployee(employee);
}
//This method return list of employees in database
@Override
@Transactional
public List<EmployeeEntity> getAllEmployees() {
return employeeDAO.getAllEmployees();
}
//Deletes a employee by it's id
@Override
@Transactional
public void deleteEmployee(Integer employeeId) {
employeeDAO.deleteEmployee(employeeId);
}
//This setter will be used by Spring context to inject the dao's instance
public void setEmployeeDAO(EmployeeDAO employeeDAO) {
this.employeeDAO = employeeDAO;
}
}
```
## 3)Spring + Hibernate 集成
现在我们必须将 Hibernate 集成到应用中。 最好的地方是利用 Spring 的强大功能进行集成,以充分利用依赖注入来与不同的 ORM 一起使用。
上面`beans.xml`文件中已经给出了 Spring 所需的 Hibernate 依赖关系。 您将需要的其他文件是:
**`hibernate.cfg.xml`**
```java
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<mapping class="com.howtodoinjava.entity.EmployeeEntity" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
```
**`jdbc.properties`**
```java
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
jdbc.databaseurl=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=password
```
**`EmployeeDaoImpl.java`**
```java
package com.howtodoinjava.dao;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.howtodoinjava.entity.EmployeeEntity;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDaoImpl implements EmployeeDAO
{
//Session factory injected by spring context
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
//This method will be called when a employee object is added
@Override
public void addEmployee(EmployeeEntity employee) {
this.sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().save(employee);
}
//This method return list of employees in database
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public List<EmployeeEntity> getAllEmployees() {
return this.sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().createQuery("from EmployeeEntity").list();
}
//Deletes a employee by it's id
@Override
public void deleteEmployee(Integer employeeId) {
EmployeeEntity employee = (EmployeeEntity) sessionFactory.getCurrentSession()
.load(EmployeeEntity.class, employeeId);
if (null != employee) {
this.sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().delete(employee);
}
}
//This setter will be used by Spring context to inject the sessionFactory instance
public void setSessionFactory(SessionFactory sessionFactory) {
this.sessionFactory = sessionFactory;
}
}
```
供您参考,`EmployeeEntity`类如下所示:
**`EmployeeEntity.java`**
```java
package com.howtodoinjava.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="EMPLOYEE")
public class EmployeeEntity {
@Id
@Column(name="ID")
@GeneratedValue
private Integer id;
@Column(name="FIRSTNAME")
private String firstname;
@Column(name="LASTNAME")
private String lastname;
@Column(name="EMAIL")
private String email;
@Column(name="TELEPHONE")
private String telephone;
//Setters and Getters
}
```
## 4)其他集成功能
除了 struts + spring + hibernate,我们还使用以下组件来构建应用。
#### a)Log4j
Spring 通过扫描类路径中的 log4j 自动配置日志记录。 我们使用`pom.xml`文件添加了 log4j 依赖项。 现在,您只需要在类路径中放置一个`log4j.xml`或`log4j.properties`文件。
**`log4j.properties`**
```java
log4j.rootLogger=info, stdout, R
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
log4j.appender.R=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.R.File=c:/log/demo.log
log4j.appender.R.MaxFileSize=100KB
log4j.appender.R.MaxBackupIndex=1
log4j.appender.R.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.R.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
```
#### b)顶级域
如果您查看`web.xml`文件,我们在其中包含了一些 TLD。 我们可以随时在视图层中使用它们,如下所示:
**`editEmployeeList.jsp`**
```java
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Spring-4 + Struts-3 + Hibernate Integration Demo</title>
<style>
table.list
{
border-collapse:collapse;
width: 40%;
}
table.list, table.list td, table.list th
{
border:1px solid gray;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Spring-4 + Struts-3 + Hibernate Integration Demo</h2>
<s:form method="post" action="add">
<table>
<tr>
<td><s:textfield key="label.firstname" name="employee.firstname"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><s:textfield key="label.lastname" name="employee.lastname"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><s:textfield key="label.email" name="employee.email"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><s:textfield key="label.telephone" name="employee.telephone"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<s:submit key="label.add"></s:submit>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</s:form>
<h3>Employees</h3>
<c:if test="${!empty employees}">
<table class="list">
<tr>
<th align="left">Name</th>
<th align="left">Email</th>
<th align="left">Telephone</th>
<th align="left">Actions</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${employees}" var="emp">
<tr>
<td>${emp.lastname}, ${emp.firstname} </td>
<td>${emp.email}</td>
<td>${emp.telephone}</td>
<td><a href="delete/${emp.id}">delete</a></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</c:if>
</body>
</html>
```
#### c)事务
`EmployeeManagerImpl.java`在诸如`getAllEmployees()`和`deleteEmployee()`之类的方法中使用注解`@Transactional`。 这实际上是在单个事务中运行在此方法下执行的所有数据库查询。 像这样在`beans.xml`上下文文件中声明了事务依赖项。
```java
<!-- Run SQL queries in transactions -->
<tx:annotation-driven />
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
```
## 5)要记住的要点
**a)如果运行时无法找到`lib`文件夹中存在的类,则将来自项目依赖项的 jar 文件添加到项目部署程序集中。**
**b)**使`bean.xml`中定义的`Action`类的**作用域为“原型”**。 Spring 提供的 bean 的默认范围是单例,并且必须为每个请求创建新的 Struts `Action`类,因为它包含特定于用户会话的数据。 为了容纳两者,请将`Action`类 bean 标记为原型。
**c)**在运行此应用之前,请不要忘记**设置数据库**。 如果安装不正确,将导致您出现一些异常。
**d)**另外,请**在项目运行时依赖项中也包括**`struts2-spring-plugin`。
## 6)教程中使用的数据库架构
下表已在 MySQL 中的名为“`test`”的数据库中创建。
```java
CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
FIRSTNAME VARCHAR(30),
LASTNAME VARCHAR(30),
TELEPHONE VARCHAR(15),
EMAIL VARCHAR(30),
CREATED TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
```
如果您打算自己构建应用,则在下面给定的**直接在此应用中使用的结构**将为您提供帮助。
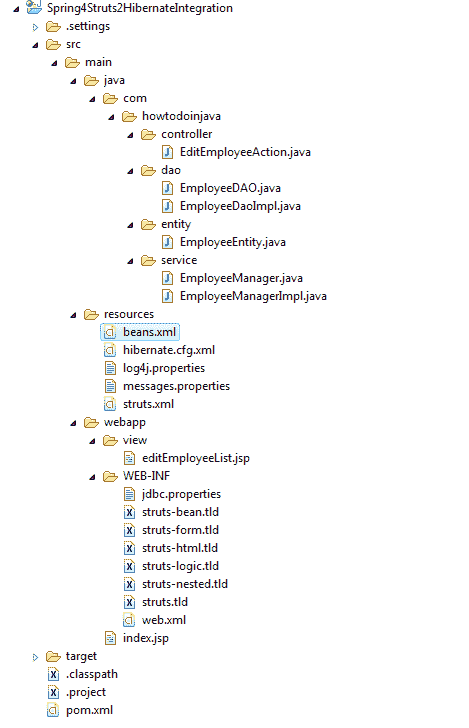
Spring Struts Hibernate 集成的目录结构
此项目中使用的`pom.xml`文件具有所有项目相关性(有些额外),如下所示:
**`pom.xml`**
```java
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.howtodoinjava.app</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring4Struts2HibernateIntegration</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Spring4Struts2HibernateIntegration Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<!-- JBoss repository for Hibernate -->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>JBoss repository</id>
<url>http://repository.jboss.org/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<properties>
<org.springframework.version>4.0.3.RELEASE</org.springframework.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId>
<artifactId>struts2-core</artifactId>
<version>2.3.16.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId>
<artifactId>struts2-spring-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3.16.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--
Core utilities used by other modules.
Define this if you use Spring Utility APIs (org.springframework.core.*/org.springframework.util.*)
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!--
Bean Factory and JavaBeans utilities (depends on spring-core)
Define this if you use Spring Bean APIs (org.springframework.beans.*)
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--
Application Context (depends on spring-core, spring-expression, spring-aop, spring-beans)
This is the central artifact for Spring's Dependency Injection Container and is generally always defined
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--
Aspect Oriented Programming (AOP) Framework (depends on spring-core, spring-beans)
Define this if you use Spring AOP APIs (org.springframework.aop.*)
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjtools</artifactId>
<version>1.6.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--
Transaction Management Abstraction (depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-aop, spring-context)
Define this if you use Spring Transactions or DAO Exception Hierarchy
(org.springframework.transaction.*/org.springframework.dao.*)
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--
JDBC Data Access Library (depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-context, spring-tx)
Define this if you use Spring's JdbcTemplate API (org.springframework.jdbc.*)
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--
Object-to-Relation-Mapping (ORM) integration with Hibernate, JPA, and iBatis.
(depends on spring-core, spring-beans, spring-context, spring-tx)
Define this if you need ORM (org.springframework.orm.*)
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.mail</groupId>
<artifactId>mail</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.jms</groupId>
<artifactId>jms</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jdmk</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxtools</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jmx</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxri</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>3.6.3.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javassist</groupId>
<artifactId>javassist</artifactId>
<version>3.12.1.GA</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbcp</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>Spring3Struts2HibernateIntegration</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
```
## 7)下载源代码
下载以上示例的源代码或获取`.war`文件。
[下载源码](https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B7yo2HclmjI4S2c5YldiNk44aVE/edit?usp=sharing "spring + struts + hibernate tutorial source code link")
[下载`.war`文件](https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B7yo2HclmjI4T2NrS19iRU5Hb3c/edit?usp=sharing "spring + struts + hibernate tutorial .war file link")
这是 **Spring4 + Struts2 + hibernate 集成**教程的全部内容。 让我知道您的想法和疑问。
**祝您学习愉快!**
- HowToDoInJava Spring 教程
- Spring 5
- Spring 5 教程
- Spring 5 的新功能和增强功能
- Spring 使用注解配置 Bean
- Spring bean – XML 配置
- Spring – @Lazy加载
- Spring DispatcherServlet – 它是如何工作的?
- Spring @PostMapping示例 – @GetMapping示例
- Spring 5 MVC + Hibernate 5 示例
- Spring 和 CORS
- Spring Security 5 – Java 配置
- Spring Security 5 登录表单示例
- Spring
- Spring 教程
- Spring – IoC 容器
- Spring – 控制反转与依赖注入
- Spring 5 – Bean 范围
- Spring – Bean 生命周期
- Spring BeanPostProcessor示例
- SpringBean 自动装配 – @Autowired
- Spring 注解
- Spring – 原型注解
- Spring @Scheduled – 安排任务的 4 种方法
- Spring 定时器任务
- Spring – 应用事件
- Spring i18n – ResourceBundleMessageSource
- Spring ResourceLoaderAware - 在 Spring 中读取文件
- Spring 属性编辑器 – CustomEditorConfigurer示例
- Spring – 使用JavaMailSender发送电子邮件
- Spring 的无版本模式(最新版本)
- Spring 面试问答
- 编写配置文件的 13 个 Spring 最佳实践
- SpringBoot 2
- SpringBoot 教程
- spring-boot-starter-parent示例
- spring-boot-starter Maven 模板
- Spring Boot 多模块 Maven 项目示例
- Spring Boot 注解
- Spring Boot2 @SpringBootApplication自动配置
- Spring Boot 和 AOP
- Spring Boot 日志指南
- Spring Boot Devtools 教程
- Spring Boot WAR 包示例
- Spring Boot 2 REST API 示例
- Spring Boot Crud 操作示例与 Hibernate
- Spring Boot 2 – OAuth2 Auth 和资源服务器
- 在 Spring Boot 2 中进行测试
- Spring RestTemplate – Spring REST 客户端示例
- Spring Boot – CRUD 应用程序
- Spring Boot Hibernate 配置示例
- Spring Boot – 数据源配置
- Spring Boot 异常处理 – @ExceptionHandler示例
- Spring Boot 缓存示例教程
- 使用 Spring Boot 的 SpringRetry 模块示例
- Spring Boot Security Rest 基本身份验证示例
- Spring Boot 和 H2 数据库
- Spring Boot 2 和 ehcache 3 示例
- Spring Boot 2 与 Gson
- Spring Boot Remoting – Spring RMI 注解示例
- SpringBoot – 发送带有附件的电子邮件
- Spring Boot 面试问题
- SpringBoot
- SpringBoot – CommandLineRunner接口示例
- Spring Boot – 配置 Jetty 服务器
- Spring Boot 更改嵌入式服务器的默认端口
- Spring Boot – 更改上下文路径
- Spring Boot SSL(HTTPS)示例
- Spring Boot – 获取所有已加载的带有类类型信息的 bean
- Spring Boot – 自定义PropertyEditor配置示例
- Spring Boot @Scheduled注解示例
- Spring Boot Jersey 示例
- Spring Boot SOAP Web 服务示例
- Spring Boot SOAP 客户端 – WebServiceTemplate示例
- 带有嵌入式 ActiveMQ 的 Spring Boot JMSTemplate
- Spring Boot Hello World 示例 – Spring Boot REST 示例
- Spring Boot JSP 视图解析器示例
- SpringBoot – 执行器
- Spring Boot – 带有 JAX-RS 注解的基于角色的安全性
- Spring Boot RSS feed 和 ROAM
- Spring Boot ehcache 2 示例
- SpringBatch
- Spring Batch + Spring Boot Java 配置示例
- Spring Batch 事件监听器
- Spring Batch ItemProcessor示例
- 使用 Spring TaskScheduler进行 Spring Batch 作业调度
- Spring Batch Quartz Java 配置示例
- Spring Batch + Quartz + H2 Jdbcjobstore 示例
- 在 Quartz 作业中注入 Spring 依赖项
- Spring Batch FlatFileItemReader – 读取 CSV 示例
- Spring Batch FlatFileItemWriter – 写入 CSV 文件
- Spring Batch MultiResourceItemReader – 读取多个 CSV 文件示例
- Spring Batch 读取后删除或存档文件
- Spring Batch 已处理记录的计数示例
- Spring Batch CSV 到数据库 – Java 注解配置示例
- Spring Cloud
- 微服务 – 定义,原理和优势
- 服务监控 – Hystrix,Eureka 管理员和 Spring Boot 管理员
- Hoverfly – 微服务虚拟化示例
- ELK 堆栈示例教程
- Docker 的 Hello World 示例
- 集成 Git 的 Spring Cloud Config Server
- 使用 Netflix Eureka 进行 Spring Cloud 服务发现
- Consul 服务注册和发现示例
- Hystrix 断路器模式 – SpringCloud
- 如何将 Spring Boot 应用程序部署到 Cloud Foundry 平台
- Netflix Zuul 示例 – Zuul API 网关模式 – Spring Cloud 教程
- Spring Cloud Zipkin 和 Sleuth 示例
- Spring cloud ribbon 和 Eureka – 客户端负载均衡器示例
- Spring AOP
- Spring AOP 教程示例
- Spring AOP – AspectJ 注解配置示例
- Spring AOP + AspectJ XML 配置示例
- Spring AOP AspectJ @Before注解示例
- Spring AOP AspectJ @After注解示例
- Spring AOP AspectJ @Around注解示例
- Spring AOP AspectJ @AfterReturning注解示例
- Spring AOP AspectJ @AfterThrowing示例
- Spring AOP 事前建议示例
- Spring AOP 事后建议示例
- Spring AOP 围绕建议示例
- Spring AOP 返回后建议示例
- Spring AOP 抛出后建议示例
- Spring AOP AspectJ 切入点表达式示例
- Spring AOP – 切面顺序
- 带有加载时织入的非公开方法上的 Spring 事务
- Spring 热门 AOP 面试问题及答案
- Spring MVC
- Spring MVC 教程
- Spring MVC Hello World 示例
- 使用 Maven 和 JSTL 的 Spring MVC Hello World 示例
- Spring @RequestMapping注解示例
- Spring MVC 自定义验证器示例
- Spring Bean 验证 – JSR-303 注解
- Spring MVC 填充和验证下拉列表示例
- Spring MVC 示例 – 显示,验证和提交表单
- Spring MessageSourceAware Java Bean 示例
- Spring MVC XmlViewResolver配置示例
- Spring MVC 国际化(i18n)和本地化(i10n)示例
- Spring MVC 拦截器示例 – XML 和 Java 注解配置
- Spring HandlerInterceptor示例
- Spring MVC 在 ajax 和 jquery 中使用进度条上传多个文件
- Spring MVC 多文件上传示例
- Spring MVC 下载文件控制器示例
- Spring MVC 面试问题与答案
- Spring MVC InternalResourceViewResolver配置示例
- Spring MVC ResourceBundleViewResolver配置示例
- Spring MVC SimpleMappingExceptionResolver示例
- Spring MVC:<context:annotation-config>与<context:component-scan>
- ContextLoaderListener与DispatcherServlet
- SpringSecurity
- SpringSecurity 教程
- 具有保护切入点的 Spring 方法安全性
- Spring Security Siteminder 预身份验证示例
- Spring Security 登录表单示例
- 使用 JSP Taglibs 的 Spring 视图层安全
- Spring Security – JDBC 用户服务示例
- Spring Security UserDetailsService示例
- Spring Security 基本身份验证示例
- 使用 JUnit 测试 Spring Security Auth
- 使用@PreAuthorize和@Secured的 Spring 方法安全性
- Spring ORM
- Spring 3.2.5 AbstractRoutingDataSource示例
- Spring 3 和 Hibernate 4 集成示例教程
- Spring Hibernate 集成示例
- Spring REST
- Spring REST JSON 响应示例
- Spring REST XML 响应示例
- Spring REST 控制器示例
- 使用 JPA 配置的 Spring REST CRUD 示例
- Spring REST 异常处理示例
- Spring REST 请求主体和参数验证示例
- Spring REST 自定义令牌认证示例
- Spring REST – 多部分上传和下载示例
- Spring REST Multipart – 多部分上传示例
- Spring REST – HTTP OPTIONS 请求处理器示例
- Spring REST – 访问被拒绝请求的 JSON 响应
- Spring RestTemplate – Spring REST 客户端示例
- Spring WebFlux
- Spring WebFlux 教程
- Spring Boot WebFlux WebSocket 示例
- 使用@WebFluxTest和WebTestClient进行 Spring Boot Webflux 测试
- HowToDoInJava Java 教程
- 核心 Java 教程
- 什么是 Java 编程语言?
- 什么是 Java JDK,JRE 和 JVM – 深入分析
- Java 命名约定
- Java 类路径
- Java 变量
- Java 运算符指南
- Java 关键字
- Java 中的数据类型
- Java 中的原始数据类型
- Java 包装器类 – 自动装箱,拆箱和转换示例
- Java 中的语句类型
- Java 控制流语句
- Java 中的标签语句
- Java 字符串类指南
- Java 创建类 – 如何创建对象?
- 如何在 Java 中创建不可变的类
- Java main()方法
- Java 注释
- Java 按值传递与按引用传递
- Java 系统属性
- Java 静态 – 变量,方法,块,类和导入语句
- Java 中的静态导入语句
- Java hashCode()和equals() – 契约,规则和最佳实践
- Java this和super之间的区别
- 32 位 Java 与 64 位 Java 之间的区别
- java.exe和javaw.exe之间的区别
- Java 查看/生成类文件的字节码
- Java 中的小端和大端
- Java 命令行参数
- 在 Java 中比较浮点数或双精度数的正确方法
- Java 递归指南
- Java 偶对
- Java 元组 – 使用 Java 中的元组
- sun.misc.Unsafe类的用法
- Java UUID 生成器示例
- Java 12 教程
- Java 12 – 新特性和增强特性
- 收集器teeing()方法示例
- 字符串indent(count) – Java 中的行左缩进
- 精简数字格式
- Java 11 教程
- Java 11 的新特性和增强特性
- String.isBlank() – 在 Java 中检查空白或空字符串
- String.lines() – 获取行流 – Java 11
- String.repeat() – 在 Java 中重复字符串 N 次
- String.strip() – 删除开头和结尾的空格
- 文件readString() API – 将文件读取为 Java 中的字符串
- 文件writeString() API – 用 Java 将字符串写入文件
- Java 10 教程
- Java 10 特性和增强特性
- Java 版本 – 基于时间的发行版本控制
- Java var – 局部变量类型推断
- Java 9 教程
- Java 9 特性和增强特性
- Java 9 – 精简字符串改进 [JEP 254]
- Java 模块教程
- Java 9 – JShell
- Java – 日期流
- Java 9 Stream API 的改进
- Java 9 中的不可变集合和工厂方法
- 接口中的私有方法 – Java 9
- Java 8 教程
- Java 8 教程
- Java 8 forEach
- Java 8 流 API
- Java 流装箱示例
- Lambda 表达式
- Java 8 – 函数式接口
- Java 8 方法引用示例
- Java 默认方法教程
- Java 8 Optional:完整参考
- Java 谓词示例 – 谓词过滤器
- Java 8 – 日期和时间示例
- Java 8 列出目录中的所有文件 – 六个示例
- Java 8 – 逐行读取文件
- Java 8 写入文件示例
- Java WatchService API 教程
- Java 8 解析字符串为日期
- Java 8 – 连接字符串数组 – 将数组转换为字符串
- Java Base64 编码和解码示例
- Math 类中的 Java 精确算术运算支持
- Java 8 带有 lambda 的Comparator示例
- 使用Pattern.compile()方法将 Java 正则表达式作为谓词
- Java 字符串连接(CSV)示例
- Java 8 两个日期之间的差异
- Java – 内部与外部迭代
- Java 中的安全随机数生成
- Java 7 教程
- Java 7 的更改,特性和增强
- Java 菱形运算符 – Java 中的<>运算符
- 带字符串的 Java switch case
- Java 7 中的try-with-resources
- Java 7 中数字字面值的下划线
- Java 抑制异常示例
- Java 7 – 异常处理增强
- Fork/Join 框架教程:ForkJoinPool示例
- 自动重新加载属性的 Java WatchService示例
- 面向对象原则
- Java OOP 概念 – 面向对象的原则
- Java 访问修饰符
- Java 构造器
- Java 实例初始化器块
- Java 中的抽象示例
- Java 封装与抽象
- Java 继承
- Java 多态示例
- Java 方法重载与方法重载
- 接口与 Java 中的抽象类
- Java extends与implements关键字
- Java instanceof运算符
- Java 中的多重继承
- 关联,聚合和组合
- Java 并发指南
- Java 并发教程
- Java 多线程的发展和主题
- Java 并发性 – 线程安全性?
- 并发与并行
- Java 比较和交换示例 – CAS 算法
- Java synchronized关键字
- Java 中的对象级别锁与类级别锁
- Java 中Runnable与Thread之间的区别
- 如何在 Java 中使用wait(),notify()和notifyAll()?
- Java 并发性 – yield()和join()之间的区别
- Java 中 sleep()和wait()之间的区别
- 锁和监视器之间的区别 – Java 并发
- Java Callable Future示例
- 如何使用UncaughtExceptionHandler重新启动线程
- 使用ThreadPoolExecutor和Semaphore限制任务提交率
- Java 执行器框架教程和最佳实践
- Java 线程间通信 – PipedReader和PipedWriter
- Java 死锁示例和解决方案
- Java 集合
- Java 中的集合
- Java 中的数组
- Java ArrayList指南
- Java LinkedList类
- Java HashMap指南
- Java Hashtable类
- Java LinkedHashMap类
- Java TreeMap类
- Java HashSet类
- Java LinkedHashSet类
- Java TreeSet类
- Java Comparable接口示例
- Java Comparator接口示例
- Java Iterator接口示例
- Java ListIterator接口
- Java Spliterator接口
- Java PriorityQueue类
- Java PriorityBlockingQueue类
- Java ArrayBlockingQueue类
- Java TransferQueue – Java LinkedTransferQueue类
- Java CopyOnWriteArrayList类
- Java CopyOnWriteArraySet类
- 如何在 Java 中对数组,列表,映射和集合进行排序
- Java 面试的 40 个热门问答集
- Java IO 教程
- Java IO 教程和示例
- Java I/O 如何在较低级别上内部工作?
- Java 标准 IO 与 Java NIO
- 如何在 Java 中复制目录
- 用 Java 递归删除目录
- Java – 创建新文件
- Java – 写入文件
- Java – 附加到文件
- Java 创建只读文件示例
- Java 将文件读取为字符串(已针对 Java 8 更新)
- Java 将文件读取到byte[]数组
- Java – 逐行读取文件 – LineNumberReader
- Java BufferedReader示例
- Java – BufferedWriter
- Java 读写属性文件示例
- 从资源文件夹读取文件 – Spring 示例
- Java – 读写 UTF-8 编码数据
- Java 中如何检查文件是否存在
- Java 文件复制 – 用 Java 复制文件的 4 种方法
- Java FilenameFilter示例 – 查找/删除某些扩展名的文件
- Java FileFilter示例
- Java – 创建临时文件
- Java – 写入临时文件
- Java – 删除临时文件
- Java – 读取控制台输入
- Java – 使用Scanner类读取类型安全输入
- 在 Java 中将字符串转换为InputStream
- 在 Java 中将InputStream转换为字符串
- Java – 创建受密码保护的 Zip 文件
- Java – 解压缩带有子目录的文件
- 使用 Java 在 Linux 中管理不超过 N GB 的系统日志文件
- 在 Java 中生成 SHA 或 MD5 文件校验和哈希
- Java 日期时间教程
- Java – 日期和时间 API
- Java – 日期验证
- Java – 日期格式
- Java LocalDate类
- Java LocalTime类
- Java LocalDateTime类
- Java ZonedDateTime类
- Java 8 – Period
- Java 8 DateTimeFormatter
- Java 8 – TemporalAdjusters
- Java 8 – TemporalQuery
- Java 8 – DayOfWeek
- Java 日期 – 解析,格式和转换
- Java 语言环境 – 创建和设置默认语言环境
- Java 枚举教程
- Java 枚举
- 带有字符串值的 Java 枚举
- 枚举真的是最好的单例吗?
- 枚举器和迭代器之间的区别?
- Java 异常
- Java try-finally块
- Java throw关键字
- Java 受检与非受检的异常
- Java 同步和异步异常
- Java NullPointerException - 如何在 Java 中有效处理空指针
- Java 自定义异常 – 最佳实践
- 构造器可以声明初始化器块中引发的受检异常
- Java 泛型教程
- 完整的 Java 泛型教程
- Java 泛型 PECS - 生产者extends消费者super
- Java 垃圾回收
- Java 垃圾收集算法(直到 Java 9)
- JVM 内存模型/结构和组件
- Java 内存管理 – 垃圾回收算法
- Java 序列化教程
- Java 序列化 – 执行正确的序列化
- Java serialVersionUID – 如何生成serialVersionUID
- Java 外部化示例 – 更有效的序列化
- Java 中Externalizable与Serializable之间的区别
- 将 Java 对象序列化为 XML – XMLEncoder和XMLDecoder示例
- Java 中反序列化过程如何发生?
- 使用readObject和writeObject的 Java 自定义序列化
- 使用内存序列化的 Java 深层复制
- 字符串方法
- Java String.concat()方法示例
- Java String.hashCode()方法示例
- Java String.contains()方法示例
- Java String.compareTo()方法示例
- Java String.compareToIgnoreCase()方法示例
- Java String.equals()方法 – 字符串比较
- Java String.equalsIgnoreCase()方法 – 不区分大小写的比较
- Java String.charAt()方法示例
- Java String.indexOf()方法示例
- Java String.lastIndexOf()方法示例
- Java String.intern()方法示例
- Java String.split()方法示例
- Java String.replace()方法示例
- Java String.replaceFirst()方法示例
- Java String.replaceAll()方法示例
- Java String.substring()方法示例
- Java String.startsWith()示例
- Java String.endsWith()方法示例
- Java String.toUpperCase()方法示例
- Java String.toLowerCase()方法示例
- Java 正则表达式教程
- Java 正则表达式教程
- Java 仅允许字母数字字符的正则表达式
- Java 正则表达式 – 信用卡号验证
- Java 正则表达式 – 加拿大邮政编码验证
- 货币符号的 Java 正则表达式
- 使用 Java 正则表达式进行日期验证
- 使用 Java 正则表达式进行电子邮件验证
- Java 正则表达式密码验证示例
- 适用于希腊语扩展或希腊语脚本的 Java 正则表达式
- 验证 ISBN(国际标准书号)的 Java 正则表达式
- 检查输入文本的最小/最大长度的 Java 正则表达式
- 限制文本中的行数的 Java 正则表达式
- 限制输入中的单词数的 Java 正则表达式
- 验证 SSN(社会安全号码)的 Java 正则表达式
- Java 正则表达式 – 英国邮政编码验证
- Java 正则表达式 – 美国邮政编码验证
- 验证商标符号的 Java 正则表达式
- 验证国际电话号码的 Java 正则表达式
- 北美电话号码的 Java 正则表达式
- Java NIO 教程
- NIO 教程
- 如何创建路径 – Java NIO
- 使用缓冲区 – Java NIO 2.0
- Java 通道教程 – NIO 2.0
- 3 种读取文件的方法 – Java NIO
- Java 8 – 逐行读取文件
- Java 内存映射文件 – Java MappedByteBuffer
- Java NIO – 分散/聚集或向量 IO
- 通道之间的数据传输 – Java NIO
- HowToDoInJava 其它教程
- Maven 教程
- 如何在 Windows 上安装 Maven
- Maven – 设置文件
- Maven – 依赖管理
- Maven 依赖范围
- Maven - POM 文件
- Maven – 父子 POM 示例
- Maven – 本地,远程和中央仓库
- Maven 本地仓库位置以及如何更改?
- M2_REPO – 在 Eclipse 中更改 Maven 仓库的位置
- Maven 代理设置 – Eclipse,命令行和全局设置
- Maven 强制最低 Java 版本
- Maven 创建 Java 项目 – 交互式与非交互式模式
- 在 Eclipse 中逐步创建 Maven Web 项目
- 多模块 Maven 项目 – 控制台
- Eclipse 中的 Maven 多模块项目
- Maven – 创建 Java 源文件夹
- Maven BOM – 物料清单依赖项
- 在 Eclipse 中导入 Maven 远程原型目录
- Eclipse 项目中的 Maven 自定义原型
- 已解决:Java 编译器级别与已安装的 Java 项目方面的版本不匹配
- Maven ant 插件 – 从pom.xml生成build.xml
- Maven IntelliJ IDEA 项目
- Spring MVC JSTL 配置示例
- Tomcat Maven 插件示例
- Maven – Spring Boot 胖/Uber Jar
- Maven Shade 插件 – UberJar/胖 Jar 示例
- Maven – 删除所有损坏的 jar/依赖项
- Gradle 教程 – 安装和 HelloWorld 示例
- Log4j2 教程
- Log4j2 JSON 配置示例
- Log4j2 属性文件示例
- Log4j2 xml 配置示例
- Log4j2 RollingFileAppender示例
- Log4j2 多个附加器示例
- Log4j2 LevelRangeFilter示例
- Log4j2 HTMLLayout配置示例
- Log4j2 ThreadContext – 相同事务的鱼标日志
- Log4j2 – 有用的转换模式示例
- 为 JUnit 测试用例配置 Log4j2
- Log4j 教程
- log4j.properties示例 – Log4j 属性文件示例
- log4j.xml示例 – Log4j xml 配置示例
- Log4j Maven 配置示例
- Log4j 日志级别 – Log4j2 日志级别示例
- Log4j ConsoleAppender配置示例
- Log4jRollingFileAppender配置示例
- Log4j SocketAppender和套接字服务器示例
- Log4j JDBCAppender – 在数据库中创建日志
- Log4j XMLLayout – 以 XML 格式创建日志
- Log4j HTMLLayout – 以 HTML 格式创建日志
- Log4j – 在运行时重新加载日志记录级别
- SLF4j 与 Log4j – 哪个更好?
- RESTEasy + Tomcat 7 + Log4j 日志记录示例
- Dropwizard 教程
- Dropwizard 教程
- Dropwizard 教程 – HelloWorld 示例
- Dropwizard – BasicAuth 安全示例
- Dropwizard 运行状况检查配置示例
- Dropwizard 客户端 – Jersey/HTTP 配置和示例
- [已解决] Dropwizard – 无法解析配置(无法将类型 ID “http”解析为子类型)
- RESTEasy 教程
- JAX-RS 2.0 教程
- RESTEasy + JBOSS 7 HelloWorld 应用
- 面向初学者的 RESTEasy 示例教程
- JAX-RS @Path URI 匹配 – 静态和正则 URI
- Java REST HATEOAS 示例
- RESTEasy + Tomcat 7 + SLF4J 日志示例
- RESTEasy + Tomcat 7 + Log4j 记录示例
- RESTEasy - 文件下载示例
- RESTEasy 文件上传 - HTML 表单示例
- RESTEasy 文件上传 - HttpClient示例
- 使用 Ajax 的 JAX-RS 自定义验证示例
- 使用 Hibernate 验证器供应器进行 RESTEasy Bean 验证
- RESTEasy ContainerRequestFilter - RESTEasy 安全过滤器示例
- RESTEasy 基本认证和授权教程
- RESTEasy JAXB XML 示例
- RESTEasy Jettison JSON 示例
- Jackson 的 RESTEasy JSON 示例
- RESTEasy ExceptionMapper – 异常处理示例
- RESTEasy 客户端 API
- 使用java.net包的 RESTful 客户端
- 使用 RESTful API 的 RESTEasy 客户端
- Apache HttpClient GET 和 POST 示例
- RESTEasy Javascript/Ajax 客户端演示
- JAX-RS 2.0 RESTEasy 3.0.2.Final 客户端 API 示例
- RESTEasy 最佳实践
- RESTEasy - 与ResteasyProviderFactory共享上下文数据
- RESTEasy ExceptionMapper – 异常处理示例
- 使用 ETag 的 RESTEasy 缓存控制示例
- RESTEasy – 启用 Gzip 压缩内容编码
- 比较 SOAP 与 RESTful Web 服务
- Jersey 教程
- Jersey HelloWorld 例子
- Jersey2 HelloWorld 示例 – Jersey2 教程
- jersey-quickstart-webapp HelloWorld 示例
- Jersey 使用过滤器记录请求和响应实体
- Jersey - 如何在 REST API 响应中设置 Cookie
- Jersey 文件下载示例 – StreamingOutput
- Jersey 文件上传示例 – Jersey2 MultiPartFeature
- Jersey - Ajax 多文件上传示例
- Jersey 异常处理 – Jersey ExceptionMapper示例
- Jersey + MOXy JSON 示例
- Jersey + JSONP 示例
- Jersey + Google Gson 示例
- Jersey REST API 安全示例
- Jersey 客户端
- Jersey 客户端示例 – Jersey2 客户端 API
- Jersey REST 客户端认证示例
- Jersey 客户端 - 设置 Cookie 示例
- JDBC 教程
- Java JDBC 教程
- Java – JDBC 连接示例(MySQL)
- Java – JDBC 驱动类型
- JDBC SELECT查询示例
- JDBC SQL INSERT查询示例
- JDBC SQL DELETE查询示例
- Java JDBC PreparedStatement示例
- JDBC 性能优化技巧
- Hiberate 教程
- Hiberate 教程
- Hibernate 示例 – HelloWorld 示例逐步简介
- Hibernate 获取实体示例 – get与load方法
- Hibernate 插入查询教程
- Hiberate 合并和刷新实体
- Hibernate 4 – 获取延迟加载的实体引用
- 从数据库中插入/选择 Blob 的 Hiberate 示例
- Hiberate save()和saveOrUpdate()方法
- Hiberate 实体/持久化生命周期状态
- Hibernate 4:如何构建SessionFactory
- Hiberate 实体等价和等同
- Hibernate JPA 级联类型
- Hibernate 延迟加载教程
- Hiberate 条件查询示例
- Hibernate HQL(Hiberate 查询语言)示例
- Hibernate @NamedQuery教程
- Hibernate – 如何定义实体之间的关联映射
- 通过示例了解 Hibernate 一级缓存
- Hiberate 二级缓存如何工作?
- Hibernate EhCache 配置教程
- Hibernate OSCache 配置示例教程
- Hibernate C3P0 连接池配置教程
- Hiberate 内存数据库
- Hibernate 验证器 – Java Bean 验证示例
- Hibernate 验证器 CDI – @HibernateValidator示例
- [已解决] UnexpectedTypeException - 找不到约束验证器
- Hiberate 注解
- Hibernate / JPA2 持久化注解教程
- Hiberate 注解与映射 – 优缺点
- @Immutable和@NaturalId – 特定于 Hiberate 的注解
- Hibernate @NaturalId示例教程
- Hiberate 一对多映射注解示例
- Hiberate 多对多映射注解示例
- Hiberate 一对一映射注解示例
- JUnit5 教程
- JUnit5 教程
- JUnit5 测试生命周期
- JUnit5 @BeforeAll注解示例
- JUnit5 @BeforeEach注解示例
- JUnit5 @AfterEach注解示例
- JUnit5 @AfterAll注解示例
- JUnit5 @RepeatedTest注解示例
- JUnit5 @Disabled测试示例
- JUnit5 @Tag注解示例
- JUnit5 预期的异常 – assertThrows()示例
- JUnit5 断言示例
- JUnit5 假设示例
- JUnit5 测试套件示例
- JUnit5 和 Gradle
- JUnit5 Maven 依赖项
- JUnit5 – 在 Eclipse 中执行测试
- Eclipse 的 JUnit5 测试模板
- JUnit5 与 JUnit4
- JUnit4 教程
- JUnit 教程
- JUnit 测试套件示例
- JUnit JUnitCore示例
- 使用 Maven 执行 JUnit 测试用例
- JUnit4 – 基于假设的测试用例
- Junit 预期异常测试用例示例
- JUnit 测试监听器– JUnit RunListener示例
- JUnit 测试超时 – JUnit5 超时示例
- JUnit 有序测试执行示例
- JUnit 参数化测试示例
- Junit 参数化测试 – @Theory和@DataPoints
- JUnit – 使用TemporaryFolder和@Rule创建临时文件/文件夹
- TestNG 教程
- TestNG 教程
- TestNG 教程(使用 Eclipse)
- 如何从 Maven 运行testng.xml
- TestNG 注解教程
- TestNG – 预期异常和预期消息教程
- TestNG – 如何禁用/忽略测试方法
- TestNG 并行执行测试,类和套件
- TestNG – 依赖测试示例
- TestNG – 超时测试教程
- TestNG @Parameters – 测试参数示例
- TestNG @DataProvider – 测试参数示例
- TestNG @Factory注解教程
- TestNG – @Factory和@DataProvider之间的区别
- TestNG 的前后注解
- TestNG – 测试组,元组,默认组示例
- Mockito 教程
- Mockito2 教程 – JUnit Mockito 示例
- Mockito 注解– @Mock,@Spy,@Captor,@InjectMock
- Mockito – @Mock和@InjectMock注解之间的区别
- Mockito – 验证具有不同参数的多个方法调用
- Spring Boot,Mockito 和 Junit – 单元测试服务层
- [已解决] IllegalStateException:无法初始化插件MockMaker
- 使用 PowerMock 进行模拟测试(带有 JUnit 和 Mockito)
- TypeScript 教程
- TypeScript 教程
- TypeScript 类型
- TypeScript 联合类型
- 字符串字面值类型
- TypeScript 变量 – var,let和const
- TypeScript 模板字符串
- TypeScript 算术运算符
- TypeScript 逻辑运算符
- TypeScript 比较运算符
- TypeScript for…of循环
- TypeScript 中的展开运算符
- TypeScript 中的数组
- TypeScript 中的枚举
- TypeScript 映射
- TypeScript 集合
- TypeScript 函数 – 剩余,可选和默认参数
- TypeScript 函数或方法重载
- 转译器(Transpiler)与编译器
- JavaScript 中的真值和假值
- 相等运算符(==)与严格相等运算符(===)
- JavaScript 中的undefined vs null
- JavaScript 变量提升
- tsconfig.json – TypeScript 编译器配置
- Angular(2.x)教程
- Angular 开发工作区设置
- [已解决] Npm 安装挂起或时间过长
- 模拟 REST 服务器来伪造在线 API
- Angular 插值
- Angular 组件
- Angular 模板和视图
- Angular 服务示例
- 带有 RxJS Observable的 Angular HttpClient示例
- AngularJS(1.x)教程
- AngularJS 教程 – HelloWorld 示例
- AngularJS – jQueryLite(jqLite)教程
- AngularJS 服务(内置和自定义)
- AngularJS Spring MVC Rest 示例
- JavaScript / jQuery 教程
- Ajax 教程 – 面向初学者的 Ajax 指南
- 完整的 jQuery Ajax($.ajax)教程
- jQuery 深度克隆示例
- jQuery 选择器 – 完整列表
- jQuery – 所有选择器(“*”) – 通用选择器
- jQuery – 检测剪切,复制或粘贴事件
- jQuery 检测ENTER键按下事件
- jQuery – Keypress和Keydown事件之间的区别
- 关于 StackOverflow 的最佳 jQuery 讨论
- JavaScript – 相等(==)与身份(===)运算符
- 您必须知道的 JavaScript 变量范围规则
- JavaScript:定义全局变量的正确方法
- 在 JavaScript 中实现 MVC 和 PubSub
- JavaScript DOM 对象与 jQuery 对象
- Jasmine 单元测试教程及示例
- JavaScript 日志 – 在 JSON 中屏蔽敏感信息
- Android 教程
- Android 教程:关键概念
- Android 教程:在 Windows 上安装 Android
- Android 教程:如何创建 Android 应用/项目
- Android 教程:Android 项目结构,文件和资源
- Android 清单:指定 Android 应用和 SDK 版本
- 如何加快缓慢的 Android AVD / 模拟器
- Hadoop 教程
- Hadoop – 大数据教程
- Hadoop MapReduce 初学者教程
- HDFS – Hadoop 分布式文件系统架构教程
- Brewer 的 CAP 定理简述
- Java 云开发简介和工具
- MongoDB 教程
- MongoDB 简介:为什么选择 MongoDB?
- 如何在 Windows 上安装 MongoDB
- Java MongoDB:使用 GridFS API 获取/保存图像
- Java MongoDB:在集合中插入文档的示例
- MongoDB 查找文档示例
- 微服务 – 定义,原理和好处
- Apache Kafka 教程
- Apache Kafka – 简介
- Apache Kafka – Windows 10 入门
- Kafka 的 Spring Boot – HelloWorld 示例
- Spring Boot Kafka JsonSerializer示例
- JMS 教程
- JMS 教程 – Java 消息服务教程
- JMS 点对点消息示例
- JMS 发布/订阅消息示例
- HornetQ 教程
- HornetQ 单体 – 基本的 JMS 消息传递示例
- 使用 Maven 的 HornetQ 独立服务器示例
- Spring3 Hornetq 独立集成示例
- Gson 教程
- Gson 教程
- Gson 安装
- GSON – 序列化和反序列化 JSON
- Gson – JSON 输出的精美打印
- GSON – 将 JSON 数组解析为 Java 数组或列表
- GSON – 序列化和反序列化 JSON 为集
- Gson – 序列化和反序列化包含自定义对象的HashMap
- Gson – GsonBuilder配置示例
- Gson - 序列化NULL值
- Gson @Since – 版本支持
- Gson @SerializedName
- Gson – 排除或忽略字段
- Gson - JsonReader
- Gson - JsonParser
- Gson – 自定义序列化和反序列化
- Gson – 快速指南
- JAXB 教程
- JAXB 注解
- JAXB @XmlRootElement注解示例
- JAXB @XmlElementWrapper注解示例
- JAXB Marshaller(编组器)示例
- JAXB Unmarshaller(解组器)示例
- JAXB 读取 XML 到 Java 对象的示例
- 使用 Moxy 和 Jaxb 将 JSON 转换为 Java 对象的示例
- JAXB 将 Java 对象写入 XML 的示例
- JAXB 将对象转换为 JSON 的示例
- JAXB – 在 Java 中编组和解组HashMap
- JAXB – 编组和解组对象列表或集合
- 使用 Eclipse 从 JAXB Java 类生成 XSD
- JAXB 模式验证
- [已解决]:javax.xml.bind.JAXBException:java.util.ArrayList或其任何超类不是此上下文的已知类
- [已解决]:线程“main”com.sun.xml.internal.bind.v2.runtime.IllegalAnnotationsException中的异常:3 个IllegalAnnotationExceptions计数
- 没有@XmlRootElement的 JAXB 编组 – 缺少@XmlRootElement错误
- 不带 jaxb 注解的解组
- Jackson 教程
- Jackson2 – 将 Java 对象转换为 JSON,并将 JSON 字符串转换为对象
- Jackson 将对象转换为 json 并将 json 转换为对象
- Jackson – 将 JSON 转换为Map并将Map转换为 JSON
- Java XML 教程
- Java 读取 XML – Java DOM 解析器示例
- Java SAX 解析器 – XML 读取示例
- Java JDOM2 – XML 读取示例
- 使用 Java StAX 解析器读取 XML – 游标和迭代器 API
- DOM 与 Java 中的 SAX 解析器
- Java 将 XML 转换为属性 – 从 XML 文件读取属性
- Java 将属性文件转换为 XML 文件
- Java 字符串到 XML – 将字符串解析为 XML DOM 的示例
- Java XML 转换为字符串 – 将 XML 对象写入文件的示例
- Java XPath 示例 – XPath 教程
- Java xpath 示例 – 在 xml 文件上求值 xpath
- Java8 xpath 示例 – 在字符串上求值 xpath
- Java XPath 表达式示例
- Java XPath NamespaceContext – 命名空间解析示例
- Java XPath 从 XML 获取属性值
- 在 Java 中使用 xpath 查找具有属性值的 xml 元素
- Java XPath – 检查节点或属性是否存在?
- Eclipse 教程
- 在 Eclipse 中导入 Maven 远程原型目录
- 使用 Eclipse 快速搜索插件进行更快的文本搜索
- 如何在 Eclipse 中显示非英文 unicode(例如中文)字符
- 如何在 Eclipse 中增加控制台输出限制
- 创建 Eclipse 模板以加快 Java 编程
- 在 5 分钟内使 Eclipse 更快
- 如何在印地语中编译和运行 Java 程序
- Java 覆盖最终静态方法 – 方法是覆盖还是隐藏?
- [已解决] 在 Eclipse 的 Java 构建路径中找不到超类“javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet”
- 版本控制系统教程
- 分布式版本控制系统如何工作?
- 版本控制系统(VCS)如何工作?
- 如何从 Google Code 项目中签出源代码
- Tomcat 教程
- Tomcat – 架构和server.xml配置
- 如何在默认的 HTTP 端口 80 中运行 tomcat
- Tomcat – 启用/禁用目录列表
- Tomcat SSL 或 HTTPS 配置示例
- 通过单个服务器安装运行 Tomcat 的多个实例
- Tomcat Maven 插件示例
- Spring,Tomcat – 获取负载均衡器后面的真实 IP
- Web 服务器如何工作?
- Linux 教程
- JStack 线程转储分析器
- 使用 Java 在 Linux 中管理系统日志文件不超过 N GB
- Swagger – Spring REST 示例
- GoF 设计模式
- 设计模式
- 创建型设计模式
- Java 单例模式介绍
- Java 中的构建器设计模式
- Java 工厂模式说明
- 抽象工厂模式解释
- Java 中的原型设计模式
- 行为型设计模式
- 责任链设计模式
- 命令设计模式
- 迭代器设计模式
- 中介者设计模式
- 备忘录设计模式
- 观察者设计模式
- 状态设计模式
- 策略设计模式
- 模板方法设计模式
- 访问者设计模式示例
- 结构型设计模式
- Java 中的适配器设计模式
- 桥接设计模式
- 组合设计模式
- Java 中的装饰器设计模式
- 外观设计模式
- 享元设计模式
- 代理设计模式
- 设计原则
- Java 中的 SOLID 原则(含示例)
- 开闭原则
- 单一责任原则
- Java 最佳实践
- Java 最佳实践指南
- 编写好的单元测试的 FIRST 原则
- 您应该如何对 DAO 层进行单元测试
- JUnit 最佳实践指南
- 不良单元测试用例的 8 个迹象
- 20 个 Java 异常处理最佳实践
- 13 个编写 Spring 配置文件的最佳实践
- Java Web 应用性能改进技巧
- Java 算法
- Java 算法和实现
- 冒泡排序 Java 示例
- 插入排序 Java 示例
- 归并排序 Java 示例
- 快速排序 Java 示例
- 选择排序 Java 示例
- Java AES 加密解密示例
- 使用 Soundex 算法实现语音搜索
- Java 比较和交换示例 – CAS 算法
- Python 教程
- Python 教程
- 如何在 Sublime 编辑器中安装 Python 包
- Python – 注释
- Python – 变量
- Python – 数据类型
- Python – 关键字
- Python – 字符串
- Python – 列表
- Python – 元组
- Python max()和min()– 在列表或数组中查找最大值和最小值
- Python 找到 N 个最大的或最小的项目
- Python 读写 CSV 文件
- Python httplib2 – HTTP GET 和 POST 示例
- Python 将元组解包为变量或参数
- Python 解包元组 – 太多值无法解包
- Python 多重字典示例 – 将单个键映射到字典中的多个值
- Python OrderedDict – 有序字典
- Python 字典交集 – 比较两个字典
- Python 优先级队列示例
- RxJava 教程
- 完整的 Java Servlet 教程
- vaadin 教程
- 使用 Maven 的 vaadin HelloWorld Web 应用
- Vaadin ComboBox示例
- vaadin 文本字段示例
- Vaadin Spring Security BasicAuth 示例
- SQL 教程
- SQL – 不使用临时表删除重复行
- 查找员工的第 N 高薪的 SQL 查询
- SQLException:用户root@localhost的访问被拒绝
- Struts2 教程
- Struts2 HelloWorld 示例
- Struts2 HelloWorld 注解示例
- 使用@InterceptorRef的 Struts2 自定义拦截器示例
- Struts2 – 如何正确设置结果路径
- Spring4 + Struts2 + Hibernate 集成教程
- [已解决] 无法找到ref-name引用的拦截器类
- [已解决]:找不到扩展名properties或xml的结果类型
- 数据结构教程
- 使用数组的 Java 栈实现
- Java 中的自定义列表实现示例
- HTML5 教程
- HTML5 – <section>标签示例
- HTML5 字符集 – 字符编码声明
- HTML5 DOCTYPE声明示例
- Java 题目
- Java 面试题目与答案
- Java 中的无效代码和无法访问的代码
- Java 字符串回文 – Java 数字回文示例
- 检测LinkedList中的无限循环的示例
- 复合赋值运算符i += j与 Java 中的i = i + j不同
- Java 中的 HiLo 猜谜游戏
- Java 题目 – 查找所有重复的元素
- Java 题目 – TreeMap的放置操作
- 题目 – 返回所有字符串中的第 N 长字符串
- Java 题目:好的字符串 – 坏的字符串
- 题目 – 检查字符串是否完整(包含所有字母)
- Java 中的反转字符串 - 单词反转字符串
- 用 Java 计算阶乘的 3 种方法
- Java 中的 FizzBuzz 解决方案
- 从 Java 中的序列/数组中查找缺失的数字
- Java – 不使用“new”关键字创建对象
- 面试问题
- Java 面试问题
- Java 字符串面试问题与答案
- Java 核心面试问题 – 第 1 部分
- Java 核心面试问题 – 第 2 部分
- Java 核心面试问题 – 第 3 部分
- Java 面试的 40 个热门问答集
- 中级开发人员的 Java 面试问题
- 针对 Oracle 企业管理器项目的实际 Java 面试问题
- HashMap和ConcurrentHashMap面试问题
- Java 版本和新特性
