在使用PostgreSQL数据库过程中,对SQL调优最常用的手段是使用explain查看执行计划,很多时候我们只关注了执行计划的结果而未深入了解执行计划是如何生成的。优化器作为数据库核心功能之一,也是数据库的“大脑”,理解优化器将有助于我们更好地优化SQL,下面将会为大家解开PostgreSQL优化器神秘的面纱。
## SQL执行过程
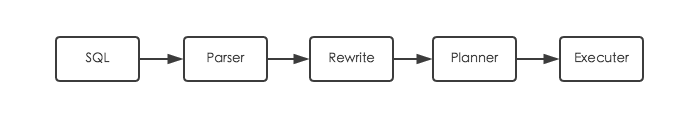
在PG数据库中,对于DDL语句无需进行优化,到utility模块处理,对于DML语句需要到优化器中处理,一个用户连接从接收SQL到执行的流程如下:
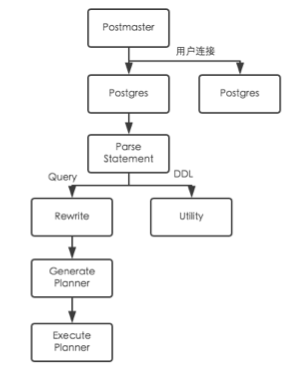
## 查询重写
主要目的是为了消除view、rule等,如下示例,视图v_t_1_2在执行计划里面已经被t1、t2替换。
~~~
create view v_t_1_2 as SELECT t1.a1, t1.b1, t2.a2, t2.b2 FROM t1, t2;
postgres=> explain select * from v_t_1_2, t1 where v_t_1_2.a1 = 10 and t1.b1 = 20; QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.55..41.59 rows=1000 width=24)
-> Nested Loop (cost=0.55..16.60 rows=1 width=16)
-> Index Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 t1_1 (cost=0.28..8.29 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (a1 = 10)
-> Index Scan using b1_1 on t1 (cost=0.28..8.29 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (b1 = 20)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=8)
(7 rows)
~~~
## 提升子链
目标是将IN和exists子句递归提升。
select * from t1 where t1.a1 in (select t2.a2 from t2 where t2.b2 = 10); 假设t2.a2为unique
转化为:
select t1.a1,t1,a2 from t1 join t2 where t1.a1=t2.a2 and t2.b2 = 10;
in子链接执行计划如下:
~~~
postgres=> explain select * from t1 where t1.a1 in (select t2.a2 from t2 where t2.b2 = 10);
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.28..25.80 rows=1 width=8)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..17.50 rows=1 width=4)
Filter: (b2 = 10)
-> Index Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..8.29 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (a1 = t2.a2)
~~~
explain select * from t1 where exists (select t2.a2 from t2 where t2.a2 = t1.a1) ; 假设t2.a2为unique
转化为:
select t1.a1, t1.b1 from t1, t2 where t1.a1=t2.a1;
exists子链接执行计划如下:
~~~
postgres=> explain select * from t1 where exists (select t2.a2 from t2 where t2.a2 = t1.a1) ;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Hash Join (cost=26.42..54.69 rows=952 width=8)
Hash Cond: (t2.a2 = t1.a1)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=4)
-> Hash (cost=14.52..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
(5 rows)
~~~
## 提升子查询
子查询和子链接区别:子查询不在表达式中子句,子链接在in/exists表达式中的子句。
select * from t1, (select * from t2) as c where t1.a1 = c.a2;
转化为:
select * from t1, t2 where t1.a1 = t2.a2;
~~~
postgres=> explain select * from t1, (select * from t2) as c where t1.a1 = c.a2;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Hash Join (cost=26.42..54.69 rows=952 width=16)
Hash Cond: (t2.a2 = t1.a1)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=8)
-> Hash (cost=14.52..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
(5 rows)
~~~
并不是所有的子查询都能提升,含有集合操作、聚合操作、sort/limit/with/group、易失函数、from为空等是不支持提升的。
如下:
~~~
postgres=> explain select t1.a1 from t1, (select a2 from t2 limit 1) as c where c.a2 = 10;
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.00..24.07 rows=952 width=4)
-> Subquery Scan on c (cost=0.00..0.03 rows=1 width=0)
Filter: (c.a2 = 10)
-> Limit (cost=0.00..0.01 rows=1 width=4)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=4)
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=4)
(6 rows)
~~~
## 化简条件
包含逻辑推理、表达式计算等

## 外连接消除(left/right/full join)
以left join为例,left join(左连接) 返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中连接字段相等的记录 ,如果右表没有匹配的记录,那么右表将会以NULL值代替,例如:
~~~
A表 B表
ID1 ID2
1 1
2
select * from A left join B on A.id1 = B.id2;
结果如下:
ID1 ID2
1 1
2 NULL
~~~
存在外连接left join
~~~
postgres=> explain select * from t1 left join t2 on true;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop Left Join (cost=0.00..11932.02 rows=952000 width=16)
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
-> Materialize (cost=0.00..20.00 rows=1000 width=8)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=8)
(4 rows)
~~~
消除外连接需要where和join条件保证右表不会有NULL值的行产生。
~~~
postgres=> explain select * from t1 left join t2 on t1.b1 = t2.b2 where t2.b2 is not NULL;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.28..23.30 rows=1 width=16)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1 width=8)
Filter: (b2 IS NOT NULL)
-> Index Scan using b1_1 on t1 (cost=0.28..8.29 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (b1 = t2.b2)
(5 rows)
~~~
## 条件下推
条件下推的目的为了连接前,元组数组尽量少,如下示例,条件已经下推到每个表上面了。
~~~
postgres=> explain select * from t1,t2 where t1.a1 < 10 and t2.a2 > 900;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Nested Loop (cost=0.55..31.20 rows=1000 width=16)
-> Index Scan using t2_a2_key on t2 (cost=0.28..10.03 rows=100 width=8)
Index Cond: (a2 > 900)
-> Materialize (cost=0.28..8.70 rows=10 width=8)
-> Index Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..8.65 rows=10 width=8)
Index Cond: (a1 < 10)
~~~
## 语义优化
当表中字段存在约束键时,PostgreSQL将会对其进行语义优化,因为查询条件有可能已经隐含满足或者不满足,例如:
~~~
create table tt1(id int not null);
postgres=> explain select * from tt1 where id is null;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on tt1 (cost=0.00..15407.02 rows=1 width=15)
Filter: (id IS NULL)
set constraint_exclusion = on;
postgres=> explain select * from tt1 where id is null;
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------
Result (cost=0.00..0.01 rows=1 width=0)
One-Time Filter: false
~~~
表tt1的id字段已经隐含了不为NULL,所以id=null这种条件可以直接返回false,PostgreSQL数据库默认并没有开启约束优化,需要设置constraint_exclusion这个参数。
## MIN/MAX优化
min/max函数在应用的使用中是非常广泛的,数据库有必要对其进行特殊优化,比如索引中已经将数据排好序了,最大最小值可以直接获取到,所以PostgreSQL对min/max函数做了一步转化。
select min(a1) from t1 转化为 select a1 from t1 order by a1 limit 1;
如果a1没有索引,那么将会是顺序扫描,不进行转化。
~~~
postgres=> explain select min(a1) from t1;
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Result (cost=0.32..0.33 rows=1 width=0)
InitPlan 1 (returns $0)
-> Limit (cost=0.28..0.32 rows=1 width=4)
-> Index Only Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..45.09 rows=952 width=4)
Index Cond: (a1 IS NOT NULL)
~~~
## group by优化
如果不对group by优化,那么将会需要对结果进行Sort或者Hash,但是如果表中数据已经是排序好的,那么将可以对其进行优化。
~~~
create index tt1_id_key on tt1 using btree ( id);
postgres=> explain select id from tt1 group by id;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Group (cost=0.42..33891.21 rows=1000102 width=4)
Group Key: id
-> Index Only Scan using tt1_id_key on tt1 (cost=0.42..31390.96 rows=1000102 width=4)
postgres=> explain select name from tt1 group by name;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Group (cost=132169.76..137170.27 rows=1000102 width=11)
Group Key: name
-> Sort (cost=132169.76..134670.02 rows=1000102 width=11)
Sort Key: name
-> Seq Scan on tt1 (cost=0.00..15407.02 rows=1000102 width=11)
~~~
## order by优化
1\. 利用索引消除order by
~~~
postgres=> explain select * from t1 order by a1;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..42.71 rows=952 width=8)
(1 row)
~~~
2\. order by下推,利用merge join实现更快的连接
~~~
postgres=> explain select * from t1,t2 where t1.b1=t2.b2 order by b1;
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------
Merge Join (cost=126.45..136.22 rows=1 width=16)
Merge Cond: (t1.b1 = t2.b2)
-> Sort (cost=61.62..64.00 rows=952 width=8)
Sort Key: t1.b1
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=8)
-> Sort (cost=64.83..67.33 rows=1000 width=8)
Sort Key: t2.b2
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=8)
(8 rows)
~~~
## distinct优化
类似于group by优化,distinct将会从Sort和Hash中选择最优的,如果字段中有索引,Sort代价可能会更低。
~~~
postgres=> explain select distinct(a1) from t1;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------
HashAggregate (cost=16.90..26.42 rows=952 width=4)
Group Key: a1
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..14.52 rows=952 width=4)
(3 rows)
postgres=> explain select distinct(name) from tt1;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Unique (cost=132169.76..137170.27 rows=1000102 width=11)
-> Sort (cost=132169.76..134670.02 rows=1000102 width=11)
Sort Key: name
-> Seq Scan on tt1 (cost=0.00..15407.02 rows=1000102 width=11)
~~~
## 集合操作优化
集合操作union被转换成Append方式。
~~~
postgres=> explain select a1 from t1 where a1 < 10 union select a2 from t2;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HashAggregate (cost=36.28..46.38 rows=1010 width=4)
Group Key: t1.a1
-> Append (cost=0.28..33.75 rows=1010 width=4)
-> Index Only Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..8.65 rows=10 width=4)
Index Cond: (a1 < 10)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=4)
postgres=> explain select a1 from t1 where a1 < 10 union all select a2 from t2;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Append (cost=0.28..23.75 rows=1010 width=4)
-> Index Only Scan using t1_a1_key on t1 (cost=0.28..8.65 rows=10 width=4)
Index Cond: (a1 < 10)
-> Seq Scan on t2 (cost=0.00..15.00 rows=1000 width=4)
~~~
## 总结
以上介绍了几种常见的PostgreSQL优化器对SQL优化的方法,这些方法更着重于SQL逻辑优化,也就是尽量对SQL进行等价或者推倒变换,以达到更有效率的执行计划。PostgreSQL优化器原理远不止这些,比如表的扫描方式选择、多表组合方式、多表组合顺序等,这些内容将会在后续的月报中继续呈现。
- 数据库内核月报目录
- 数据库内核月报 - 2016/09
- MySQL · 社区贡献 · AliSQL那些事儿
- PetaData · 架构体系 · PetaData第二代低成本存储体系
- MySQL · 社区动态 · MariaDB 10.2 前瞻
- MySQL · 特性分析 · 执行计划缓存设计与实现
- PgSQL · 最佳实践 · pg_rman源码浅析与使用
- MySQL · 捉虫状态 · bug分析两例
- PgSQL · 源码分析 · PG优化器浅析
- MongoDB · 特性分析· Sharding原理与应用
- PgSQL · 源码分析 · PG中的无锁算法和原子操作应用一则
- SQLServer · 最佳实践 · TEMPDB的设计
- 数据库内核月报 - 2016/08
- MySQL · 特性分析 ·MySQL 5.7新特性系列四
- PgSQL · PostgreSQL 逻辑流复制技术的秘密
- MySQL · 特性分析 · MyRocks简介
- GPDB · 特性分析· Greenplum 备份架构
- SQLServer · 最佳实践 · RDS for SQLServer 2012权限限制提升与改善
- TokuDB · 引擎特性 · REPLACE 语句优化
- MySQL · 专家投稿 · InnoDB物理行中null值的存储的推断与验证
- PgSQL · 实战经验 · 旋转门压缩算法在PostgreSQL中的实现
- MySQL · 源码分析 · Query Cache并发处理
- PgSQL · 源码分析· pg_dump分析
- 数据库内核月报 - 2016/07
- MySQL · 特性分析 ·MySQL 5.7新特性系列三
- MySQL · 特性分析 · 5.7 代价模型浅析
- PgSQL · 实战经验 · 分组TOP性能提升44倍
- MySQL · 源码分析 · 网络通信模块浅析
- MongoDB · 特性分析 · 索引原理
- SQLServer · 特性分析 · XML与JSON应用比较
- MySQL · 最佳实战 · 审计日志实用案例分析
- MySQL · 性能优化 · 条件下推到物化表
- MySQL · 源码分析 · Query Cache内部剖析
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 备库1206错误问题说明
- 数据库内核月报 - 2016/06
- MySQL · 特性分析 · innodb 锁分裂继承与迁移
- MySQL · 特性分析 ·MySQL 5.7新特性系列二
- PgSQL · 实战经验 · 如何预测Freeze IO风暴
- GPDB · 特性分析· Filespace和Tablespace
- MariaDB · 新特性 · 窗口函数
- MySQL · TokuDB · checkpoint过程
- MySQL · 特性分析 · 内部临时表
- MySQL · 最佳实践 · 空间优化
- SQLServer · 最佳实践 · 数据库实现大容量插入的几种方式
- 数据库内核月报 - 2016/05
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · 基于InnoDB的物理复制实现
- MySQL · 特性分析 · MySQL 5.7新特性系列一
- PostgreSQL · 特性分析 · 逻辑结构和权限体系
- MySQL · 特性分析 · innodb buffer pool相关特性
- PG&GP · 特性分析 · 外部数据导入接口实现分析
- SQLServer · 最佳实践 · 透明数据加密在SQLServer的应用
- MySQL · TokuDB · 日志子系统和崩溃恢复过程
- MongoDB · 特性分析 · Sharded cluster架构原理
- PostgreSQL · 特性分析 · 统计信息计算方法
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · left-join多表导致crash
- 数据库内核月报 - 2016/04
- MySQL · 参数故事 · innodb_additional_mem_pool_size
- GPDB · 特性分析 · Segment事务一致性与异常处理
- GPDB · 特性分析 · Segment 修复指南
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 并行复制外键约束问题二
- PgSQL · 性能优化 · 如何潇洒的处理每天上百TB的数据增量
- Memcached · 最佳实践 · 热点 Key 问题解决方案
- MongoDB · 最佳实践 · 短连接Auth性能优化
- MySQL · 最佳实践 · RDS 只读实例延迟分析
- MySQL · TokuDB · TokuDB索引结构--Fractal Tree
- MySQL · TokuDB · Savepoint漫谈
- 数据库内核月报 - 2016/03
- MySQL · TokuDB · 事务子系统和 MVCC 实现
- MongoDB · 特性分析 · MMAPv1 存储引擎原理
- PgSQL · 源码分析 · 优化器逻辑推理
- SQLServer · BUG分析 · Agent 链接泄露分析
- Redis · 特性分析 · AOF Rewrite 分析
- MySQL · BUG分析 · Rename table 死锁分析
- MySQL · 物理备份 · Percona XtraBackup 备份原理
- GPDB · 特性分析· GreenPlum FTS 机制
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · 备库Seconds_Behind_Master计算
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · MySQL 锁问题最佳实践
- 数据库内核月报 - 2016/02
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB 文件系统之文件物理结构
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB 文件系统之IO系统和内存管理
- MySQL · 特性分析 · InnoDB transaction history
- PgSQL · 会议见闻 · PgConf.Russia 2016 大会总结
- PgSQL · 答疑解惑 · PostgreSQL 9.6 并行查询实现分析
- MySQL · TokuDB · TokuDB之黑科技工具
- PgSQL · 性能优化 · PostgreSQL TPC-C极限优化玩法
- MariaDB · 版本特性 · MariaDB 的 GTID 介绍
- MySQL · 特性分析 · 线程池
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · mysqldump tips 两则
- 数据库内核月报 - 2016/01
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB 事务锁系统简介
- GPDB · 特性分析· GreenPlum Primary/Mirror 同步机制
- MySQL · 专家投稿 · MySQL5.7 的 JSON 实现
- MySQL · 特性分析 · 优化器 MRR & BKA
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · 物理备份死锁分析
- MySQL · TokuDB · Cachetable 的工作线程和线程池
- MySQL · 特性分析 · drop table的优化
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · GTID不一致分析
- PgSQL · 特性分析 · Plan Hint
- MariaDB · 社区动态 · MariaDB on Power8 (下)
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/12
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB 事务子系统介绍
- PgSQL · 特性介绍 · 全文搜索介绍
- MongoDB · 捉虫动态 · Kill Hang问题排查记录
- MySQL · 参数优化 ·RDS MySQL参数调优最佳实践
- PgSQL · 特性分析 · 备库激活过程分析
- MySQL · TokuDB · 让Hot Backup更完美
- PgSQL · 答疑解惑 · 表膨胀
- MySQL · 特性分析 · Index Condition Pushdown (ICP)
- MariaDB · 社区动态 · MariaDB on Power8
- MySQL · 特性分析 · 企业版特性一览
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/11
- MySQL · 社区见闻 · OOW 2015 总结 MySQL 篇
- MySQL · 特性分析 · Statement Digest
- PgSQL · 答疑解惑 · PostgreSQL 用户组权限管理
- MySQL · 特性分析 · MDL 实现分析
- PgSQL · 特性分析 · full page write 机制
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · MySQL 外键异常分析
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · MySQL 优化器 range 的代价计算
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · ORDER/GROUP BY 导致 mysqld crash
- MySQL · TokuDB · TokuDB 中的行锁
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · order by limit 造成优化器选择索引错误
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/10
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB 全文索引简介
- MySQL · 特性分析 · 跟踪Metadata lock
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · 索引过滤性太差引起CPU飙高分析
- PgSQL · 特性分析 · PG主备流复制机制
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · start slave crash 诊断分析
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 删除索引导致表无法打开
- PgSQL · 特性分析 · PostgreSQL Aurora方案与DEMO
- TokuDB · 捉虫动态 · CREATE DATABASE 导致crash问题
- PgSQL · 特性分析 · pg_receivexlog工具解析
- MySQL · 特性分析 · MySQL权限存储与管理
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/09
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB Adaptive hash index介绍
- PgSQL · 特性分析 · clog异步提交一致性、原子操作与fsync
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · BUG 几例
- PgSQL · 答疑解惑 · 诡异的函数返回值
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 建表过程中crash造成重建表失败
- PgSQL · 特性分析 · 谈谈checkpoint的调度
- MySQL · 特性分析 · 5.6 并行复制恢复实现
- MySQL · 备库优化 · relay fetch 备库优化
- MySQL · 特性分析 · 5.6并行复制事件分发机制
- MySQL · TokuDB · 文件目录谈
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/08
- MySQL · 社区动态 · InnoDB Page Compression
- PgSQL · 答疑解惑 · RDS中的PostgreSQL备库延迟原因分析
- MySQL · 社区动态 · MySQL5.6.26 Release Note解读
- PgSQL · 捉虫动态 · 执行大SQL语句提示无效的内存申请大小
- MySQL · 社区动态 · MariaDB InnoDB表空间碎片整理
- PgSQL · 答疑解惑 · 归档进程cp命令的core文件追查
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · open file limits
- MySQL · TokuDB · 疯狂的 filenum++
- MySQL · 功能分析 · 5.6 并行复制实现分析
- MySQL · 功能分析 · MySQL表定义缓存
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/07
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · Innodb change buffer介绍
- MySQL · TokuDB · TokuDB Checkpoint机制
- PgSQL · 特性分析 · 时间线解析
- PgSQL · 功能分析 · PostGIS 在 O2O应用中的优势
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB index lock前世今生
- MySQL · 社区动态 · MySQL内存分配支持NUMA
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · 外键删除bug分析
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · MySQL logical read-ahead
- MySQL · 功能介绍 · binlog拉取速度的控制
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · 浮点型的显示问题
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/06
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB 崩溃恢复过程
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 唯一键约束失效
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · ALTER IGNORE TABLE导致主备不一致
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · MySQL Sort 分页
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · binlog event 中的 error code
- PgSQL · 功能分析 · Listen/Notify 功能
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 任性的 normal shutdown
- PgSQL · 追根究底 · WAL日志空间的意外增长
- MySQL · 社区动态 · MariaDB Role 体系
- MySQL · TokuDB · TokuDB数据文件大小计算
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/05
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB redo log漫游
- MySQL · 专家投稿 · MySQL数据库SYS CPU高的可能性分析
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 5.6 与 5.5 InnoDB 不兼容导致 crash
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · InnoDB 预读 VS Oracle 多块读
- PgSQL · 社区动态 · 9.5 新功能BRIN索引
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · MySQL DDL BUG
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · set names 都做了什么
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 临时表操作导致主备不一致
- TokuDB · 引擎特性 · zstd压缩算法
- MySQL · 答疑解惑 · binlog 位点刷新策略
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/04
- MySQL · 引擎特性 · InnoDB undo log 漫游
- TokuDB · 产品新闻 · RDS TokuDB小手册
- PgSQL · 社区动态 · 说一说PgSQL 9.4.1中的那些安全补丁
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 连接断开导致XA事务丢失
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · GTID下slave_net_timeout值太小问题
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · Relay log 中 GTID group 完整性检测
- MySQL · 答疑释惑 · UPDATE交换列单表和多表的区别
- MySQL · 捉虫动态 · 删被引用索引导致crash
- MySQL · 答疑释惑 · GTID下auto_position=0时数据不一致
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/03
- MySQL · 答疑释惑· 并发Replace into导致的死锁分析
- MySQL · 性能优化· 5.7.6 InnoDB page flush 优化
- MySQL · 捉虫动态· pid file丢失问题分析
- MySQL · 答疑释惑· using filesort VS using temporary
- MySQL · 优化限制· MySQL index_condition_pushdown
- MySQL · 捉虫动态·DROP DATABASE外键约束的GTID BUG
- MySQL · 答疑释惑· lower_case_table_names 使用问题
- PgSQL · 特性分析· Logical Decoding探索
- PgSQL · 特性分析· jsonb类型解析
- TokuDB ·引擎机制· TokuDB线程池
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/02
- MySQL · 性能优化· InnoDB buffer pool flush策略漫谈
- MySQL · 社区动态· 5.6.23 InnoDB相关Bugfix
- PgSQL · 特性分析· Replication Slot
- PgSQL · 特性分析· pg_prewarm
- MySQL · 答疑释惑· InnoDB丢失自增值
- MySQL · 答疑释惑· 5.5 和 5.6 时间类型兼容问题
- MySQL · 捉虫动态· 变量修改导致binlog错误
- MariaDB · 特性分析· 表/表空间加密
- MariaDB · 特性分析· Per-query variables
- TokuDB · 特性分析· 日志详解
- 数据库内核月报 - 2015/01
- MySQL · 性能优化· Group Commit优化
- MySQL · 新增特性· DDL fast fail
- MySQL · 性能优化· 启用GTID场景的性能问题及优化
- MySQL · 捉虫动态· InnoDB自增列重复值问题
- MySQL · 优化改进· 复制性能改进过程
- MySQL · 谈古论今· key分区算法演变分析
- MySQL · 捉虫动态· mysql client crash一例
- MySQL · 捉虫动态· 设置 gtid_purged 破坏AUTO_POSITION复制协议
- MySQL · 捉虫动态· replicate filter 和 GTID 一起使用的问题
- TokuDB·特性分析· Optimize Table
- 数据库内核月报 - 2014/12
- MySQL· 性能优化·5.7 Innodb事务系统
- MySQL· 踩过的坑·5.6 GTID 和存储引擎那会事
- MySQL· 性能优化·thread pool 原理分析
- MySQL· 性能优化·并行复制外建约束问题
- MySQL· 答疑释惑·binlog event有序性
- MySQL· 答疑释惑·server_id为0的Rotate
- MySQL· 性能优化·Bulk Load for CREATE INDEX
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·Opened tables block read only
- MySQL· 优化改进· GTID启动优化
- TokuDB· Binary Log Group Commit with TokuDB
- 数据库内核月报 - 2014/11
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·OPTIMIZE 不存在的表
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·SIGHUP 导致 binlog 写错
- MySQL· 5.7改进·Recovery改进
- MySQL· 5.7特性·高可用支持
- MySQL· 5.7优化·Metadata Lock子系统的优化
- MySQL· 5.7特性·在线Truncate undo log 表空间
- MySQL· 性能优化·hash_scan 算法的实现解析
- TokuDB· 版本优化· 7.5.0
- TokuDB· 引擎特性· FAST UPDATES
- MariaDB· 性能优化·filesort with small LIMIT optimization
- 数据库内核月报 - 2014/10
- MySQL· 5.7重构·Optimizer Cost Model
- MySQL· 系统限制·text字段数
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·binlog重放失败
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·从库OOM
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·崩溃恢复失败
- MySQL· 功能改进·InnoDB Warmup特性
- MySQL· 文件结构·告别frm文件
- MariaDB· 新鲜特性·ANALYZE statement 语法
- TokuDB· 主备复制·Read Free Replication
- TokuDB· 引擎特性·压缩
- 数据库内核月报 - 2014/09
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·GTID 和 DELAYED
- MySQL· 限制改进·GTID和升级
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·GTID 和 binlog_checksum
- MySQL· 引擎差异·create_time in status
- MySQL· 参数故事·thread_concurrency
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·auto_increment
- MariaDB· 性能优化·Extended Keys
- MariaDB·主备复制·CREATE OR REPLACE
- TokuDB· 参数故事·数据安全和性能
- TokuDB· HA方案·TokuDB热备
- 数据库内核月报 - 2014/08
- MySQL· 参数故事·timed_mutexes
- MySQL· 参数故事·innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·Count(Distinct) ERROR
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·mysqldump BUFFER OVERFLOW
- MySQL· 捉虫动态·long semaphore waits
- MariaDB·分支特性·支持大于16K的InnoDB Page Size
- MariaDB·分支特性·FusionIO特性支持
- TokuDB· 性能优化·Bulk Fetch
- TokuDB· 数据结构·Fractal-Trees与LSM-Trees对比
- TokuDB·社区八卦·TokuDB团队
